The Pathophysiology of Rett Syndrome With a Focus on Breathing Dysfunctions
- PMID: 33052774
- PMCID: PMC7864239
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00008.2020
The Pathophysiology of Rett Syndrome With a Focus on Breathing Dysfunctions
Abstract
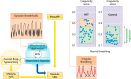
Rett syndrome (RTT), an X-chromosome-linked neurological disorder, is characterized by serious pathophysiology, including breathing and feeding dysfunctions, and alteration of cardiorespiratory coupling, a consequence of multiple interrelated disturbances in the genetic and homeostatic regulation of central and peripheral neuronal networks, redox state, and control of inflammation. Characteristic breath-holds, obstructive sleep apnea, and aerophagia result in intermittent hypoxia, which, combined with mitochondrial dysfunction, causes oxidative stress-an important driver of the clinical presentation of RTT.
Keywords: autonomic dysregulation; breathing; dysphagia; oxidative stress.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

