Superficial Temporal Artery Perforator Flap: Indications, Surgical Outcomes, and Donor Site Morbidity
- PMID: 33053764
- PMCID: PMC7712319
- DOI: 10.3390/dj8040117
Superficial Temporal Artery Perforator Flap: Indications, Surgical Outcomes, and Donor Site Morbidity
Abstract
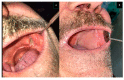
The aim of this retrospective case series was to discuss indications, surgical outcomes, and donor site morbidity in the use of superficial temporal artery perforator (STAP) flaps in intra-oral or extra-oral facial reconstruction. This study involved 9 patients treated with a STAP flap at the Maxillo-Facial Surgery Unit of the University of Campania "Luigi Vanvitelli", Naples. A STAP flap was used alone or in combination with other local flaps, for the coverage of facial soft tissue defects, after the resection of craniofacial malignant tumors (n = 7) or as a salvage flap, in partial or total microvascular flap loss (n = 2). The STAP flap was proven to be a valuable surgical option despite it not being frequently used in facial soft tissue reconstruction nor was it chosen as the first surgical option in patients under 70 year's old. Donor site morbidity is one of the major reasons why this flap is uncommon. Appropriate patient selection, surgical plan, and post-surgical touch-ups should be performed in order to reduce donor site scar morbidity.
Keywords: donor site morbidity; free flap combination; intraoral defect; reconstructive surgical procedures; superficial temporal artery island flap.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Mustarde J.C. Cheek rotation skin flap to the lower eyelid. In: Strauch B., editor. Grabb’s Encyclopedia of Flaps. Little Brown; Boston, MA, USA: 1990. p. 51.
-
- Esposito L., Razzano S., Lo Faro C., Dell’Aversana Orabona G., Schonauer F. Pinna fillet flap after advanced external ear tumor resection. JPRAS Open. 2016;8:9–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jpra.2016.02.002. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

