No association between ECSIT germline mutations and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 33054138
- PMCID: PMC8168500
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2020.269209
No association between ECSIT germline mutations and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma
Figures
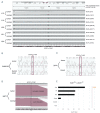
References
-
- Jin Z, Wang Y, Wang J, et al. . Multivariate analysis of prognosis for patients with natural killer/T cell lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Hematology. 2018;23(4):228-234. - PubMed
-
- Wen H, Ma H, Cai Q, et al. . Recurrent ECSIT mutation encoding V140A triggers hyperinflammation and promotes hemophagocytic syndrome in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma. Nat Med. 2018; 24(2):154-164. - PubMed
-
- Jiang L, Gu ZH, Yan ZX, et al. . Exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of DDX3X in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Nat Genet. 2015;47(9):1061-1066. - PubMed
-
- Kim S, Scheffler K, Halpern AL, et al. . Strelka2: fast and accurate calling of germline and somatic variants. Nat Methods. 2018;15(8):591-594. - PubMed
-
- Henter JI, Horne A, Arico M, et al. . HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007;48(2):124-131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

