Cytokinocytes: the diverse contribution of keratinocytes to immune responses in skin
- PMID: 33055429
- PMCID: PMC7605526
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.142067
Cytokinocytes: the diverse contribution of keratinocytes to immune responses in skin
Abstract
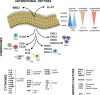
The skin serves as the primary interface between our body and the external environment and acts as a barrier against entry of physical agents, chemicals, and microbes. Keratinocytes make up the main cellular constitute of the outermost layer of the skin, contributing to the formation of the epidermis, and they are crucial for maintaining the integrity of this barrier. Beyond serving as a physical barrier component, keratinocytes actively participate in maintaining tissue homeostasis, shaping, amplifying, and regulating immune responses in skin. Keratinocytes act as sentinels, continuously monitoring changes in the environment, and, through microbial sensing, stretch, or other physical stimuli, can initiate a broad range of inflammatory responses via secretion of various cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. This diverse function of keratinocytes contributes to the highly variable clinical manifestation of skin immune responses. In this Review, we highlight the highly diverse functions of epidermal keratinocytes and their contribution to various immune-mediated skin diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Kanitakis J. Anatomy, histology and immunohistochemistry of normal human skin. Eur J Dermatol. 2002;12(4):390–399. - PubMed
-
- Rosso JD, Zeichner J, Alexis A, Cohen D, Berson D. Understanding the epidermal barrier in healthy and compromised skin: clinically relevant information for the dermatology practitioner: proceedings of an expert panel roundtable meeting. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9(4 Suppl 1):S2–S8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wickett RR, Visscher MO. Structure and function of the epidermal barrier. Am J Infect Control. 2006;34(10):S98–S110. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2006.05.295. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR073196/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR039750/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130025/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR063852/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR055508/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR070590/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007197/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR063437/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR069071/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR062546/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR071384/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR075043/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR072129/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States

