Thrombocytopenia Caused by Dexamethasone in a Patient with Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 33055471
- PMCID: PMC7662045
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.4785-20
Thrombocytopenia Caused by Dexamethasone in a Patient with Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
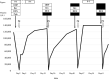
Drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia (DITP) is an important cause of thrombocytopenia. A 73-year-old man with relapsed rectal carcinoma received S-1, oxaliplatin and bevacizumab combination therapy (SOX+Bev). Dexamethasone was administered as an antiemetic prophylaxis. On day 2 of the first cycle, thrombocytopenia (8,000/μL) was observed. We sequentially omitted any drugs suspected to possibly induce thrombocytopenia and confirmed dexamethasone as the cause of thrombocytopenia. DITP induced by synthetic corticosteroids is very rare and this is the first case report of DITP induced by dexamethasone. Although rare, DITP due to synthetic corticosteroids including dexamethasone should be a differential diagnosis among patients receiving synthetic corticosteroids with thrombocytopenia.
Keywords: dexamethasone; drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
Koichi Akashi: Honoraria, Astellas Pharma, AbbVie, Eisai, Kyowa Kirin, Novartis Pharma, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo, Amgen Astellas BioPharma and Ono Pharmaceutical; Research funding, Kyowa Kirin, Shino-Test, Canon Medical Systems, Astellas Pharma, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb and Chugai Pharmaceutical. Eishi Baba: Honoraria, Eli Lilly Japan.
Figures
References
-
- van den Bemt PMLA, Meyboom RHB, Egberts ACG. Drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia. Drug Saf 27: 1243-1252, 2004. - PubMed
-
- George JN, Raskob GE, Shah SR, et al. . Drug-induced thrombocytopenia: a systematic review of published case reports. Ann Intern Med 129: 886-890, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Royer B, Lee K, Gruson B, et al. . Methylprednisolone-induced immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 115: 5431-5432, 2010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous