Design and in vivo evaluation of a microparticulate depot formulation of buprenorphine for veterinary use
- PMID: 33057103
- PMCID: PMC7560740
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-74230-6
Design and in vivo evaluation of a microparticulate depot formulation of buprenorphine for veterinary use
Abstract
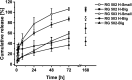
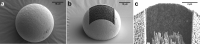
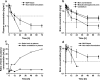
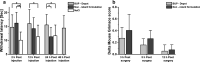
Buprenorphine is a frequently used analgetic agent in veterinary medicine. A major drawback, however, is the short duration of action requiring several daily administrations. We therefore designed a poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) based microparticulate drug formulation for sustained parenteral drug release. Particles were designed to allow for a fast onset of action and a duration of the analgesic effect of at least two days in laboratory mice. Microparticles were produced using a solvent evaporation technique. Release rate was dependent on polymer type and particle size. Spherical particles used for subsequent animal studies had a mean size of 50 µm and contained 4.5% of buprenorphine. Drug release was characterized by an initial burst release of 30% followed by complete release over seven days. In vivo pharmacokinetic experiments in female C57BL/6 J mice confirmed prolonged exposure in plasma and brain tissue and correlated with the pharmacological effect in the hot plate assay or after minor abdominal surgery. No adverse side effects with respect to food and water intake, body weight, local tolerability, or nesting behavior were observed. Our formulation is an attractive alternative to established immediate release formulations. A use for prolonged pain management in laboratory animals is proposed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microporous microsphere-based depot formulation of a peptide-like antineoplastic agent.J Microencapsul. 2002 Jul-Aug;19(4):523-35. doi: 10.1080/02652040210141084. J Microencapsul. 2002. PMID: 12396388
-
A smart approach to enable preclinical studies in pharmaceutical industry: PLGA-based extended release formulation platform for subcutaneous applications.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2020 Apr;46(4):635-645. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2020.1742146. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32163304
-
Production of Lysozyme-PLGA-Loaded Microparticles for Controlled Release Using Hot-Melt Extrusion.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020 Oct 6;21(7):274. doi: 10.1208/s12249-020-01816-8. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020. PMID: 33033873
-
Sustained-Release Hydromorphone Microparticles Produced by Supercritical Fluid Polymer Encapsulation.J Pharm Sci. 2019 Feb;108(2):811-814. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2018.09.021. Epub 2018 Sep 26. J Pharm Sci. 2019. PMID: 30267781
-
Opioids and the management of chronic severe pain in the elderly: consensus statement of an International Expert Panel with focus on the six clinically most often used World Health Organization Step III opioids (buprenorphine, fentanyl, hydromorphone, methadone, morphine, oxycodone).Pain Pract. 2008 Jul-Aug;8(4):287-313. doi: 10.1111/j.1533-2500.2008.00204.x. Epub 2008 May 23. Pain Pract. 2008. PMID: 18503626
Cited by
-
Current practices of pain assessment and analgesic use in laboratory mice: A 2022 FELASA Working Group survey.Lab Anim. 2025 Jun;59(3):396-412. doi: 10.1177/00236772241300779. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Lab Anim. 2025. PMID: 39877966 Free PMC article.
-
Development of opioid analgesic tolerance in rat to extended-release buprenorphine formulated for laboratory subjects.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 21;19(3):e0298819. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298819. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38512918 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Future: Opportunities in Long-Acting Injectable Drug Development for Veterinary Care.Pharmaceutics. 2025 May 8;17(5):626. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17050626. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40430917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Refining pain management in mice by comparing multimodal analgesia and NSAID monotherapy for neurosurgical procedures.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 12;14(1):18691. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69075-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39134625 Free PMC article.
-
A buprenorphine depot formulation provides effective sustained post-surgical analgesia for 72 h in mouse femoral fracture models.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 7;13(1):3824. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30641-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36882427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buprenorphine: a reappraisal of its antinociceptive effects and therapeutic use in alleviating post-operative pain in animals. Lab. Anim.36, 322–343 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

