Cell-type-specific 3D epigenomes in the developing human cortex
- PMID: 33057195
- PMCID: PMC7704572
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2825-4
Cell-type-specific 3D epigenomes in the developing human cortex
Abstract
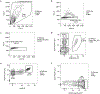
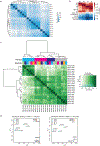
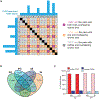
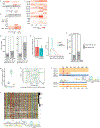
Lineage-specific epigenomic changes during human corticogenesis have been difficult to study owing to challenges with sample availability and tissue heterogeneity. For example, previous studies using single-cell RNA sequencing identified at least 9 major cell types and up to 26 distinct subtypes in the dorsal cortex alone1,2. Here we characterize cell-type-specific cis-regulatory chromatin interactions, open chromatin peaks, and transcriptomes for radial glia, intermediate progenitor cells, excitatory neurons, and interneurons isolated from mid-gestational samples of the human cortex. We show that chromatin interactions underlie several aspects of gene regulation, with transposable elements and disease-associated variants enriched at distal interacting regions in a cell-type-specific manner. In addition, promoters with increased levels of chromatin interactivity-termed super-interactive promoters-are enriched for lineage-specific genes, suggesting that interactions at these loci contribute to the fine-tuning of transcription. Finally, we develop CRISPRview, a technique that integrates immunostaining, CRISPR interference, RNAscope, and image analysis to validate cell-type-specific cis-regulatory elements in heterogeneous populations of primary cells. Our findings provide insights into cell-type-specific gene expression patterns in the developing human cortex and advance our understanding of gene regulation and lineage specification during this crucial developmental window.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG057497/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009391/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH106611/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG010972/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL129132/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH114825/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS097305/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG009402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD021822/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA200060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD079124/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HG010065/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 DA027995/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 ES026699/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007175/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY002162/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063720/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY027789/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG007175/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

