Toxoplasma gondii seropositivity and serointensity and cognitive function in adults
- PMID: 33057346
- PMCID: PMC7561134
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008733
Toxoplasma gondii seropositivity and serointensity and cognitive function in adults
Abstract
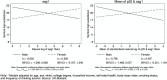
Infecting approximately one-third of the world's human population, Toxoplasma gondii has been associated with cognitive function. Here, we sought to further characterize the association between Toxoplasma gondii and cognitive function in a community sample of adults aged approximately 40 to70 years. Using adjusted linear regression models, we found associations of Toxoplasma gondii seropositivity with worse reasoning (b = -.192, p < .05) and matrix pattern completion (b = -.681, p < .01), of higher anti-Toxoplasma gondii p22 antibody levels with worse reasoning (b = -.078, p < .01) and slower Trails (numeric) performance (b = 5.962, p < .05), of higher anti-Toxoplasma gondii sag1 levels with worse reasoning (b = -.081, p < .05) and worse matrix pattern completion (b = -.217, p < .05), and of higher mean of the anti-Toxoplasma gondii p22 and sag1 levels with worse reasoning (b = -.112, p < .05), slower Trails (numeric) performance (b = 9.195, p < .05), and worse matrix pattern completion (b = -.245, p < .05). Neither age nor educational attainment moderated associations between the measures of Toxoplasma gondii seropositivity or serointensity. Sex, however, moderated the association between the sag1 titer and digit-symbol substitution and the association between the mean of the p22 and sag1 levels and digit-symbol substitution, and income moderated the association between Toxoplasma gondii seropositivity and numeric memory and the association between the p22 level and symbol-digit substitution. Based on the available neuropsychological tasks in this study, Toxoplasma gondii seropositivity and serointensity were associated with some aspects of poorer executive function in adults.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Bellou V, Belbasis L, Tzoulaki I, Middleton LT, Ioannidis JPA, Evangelou E. Systematic evaluation of the associations between environmental risk factors and dementia: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Alzheimer's & dementia: the journal of the Alzheimer's Association. 2017;13(4):406–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

