Suppression of Metacaspase- and Autophagy-Dependent Cell Death Improves Stress-Induced Microspore Embryogenesis in Brassica napus
- PMID: 33057654
- PMCID: PMC7861468
- DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pcaa128
Suppression of Metacaspase- and Autophagy-Dependent Cell Death Improves Stress-Induced Microspore Embryogenesis in Brassica napus
Abstract
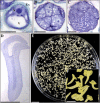
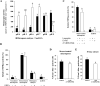
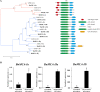
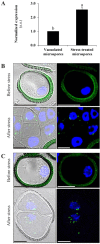
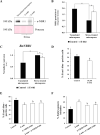
Microspore embryogenesis is a biotechnological process that allows us to rapidly obtain doubled-haploid plants for breeding programs. The process is initiated by the application of stress treatment, which reprograms microspores to embark on embryonic development. Typically, a part of the microspores undergoes cell death that reduces the efficiency of the process. Metacaspases (MCAs), a phylogenetically broad group of cysteine proteases, and autophagy, the major catabolic process in eukaryotes, are critical regulators of the balance between cell death and survival in various organisms. In this study, we analyzed the role of MCAs and autophagy in cell death during stress-induced microspore embryogenesis in Brassica napus. We demonstrate that this cell death is accompanied by the transcriptional upregulation of three BnMCA genes (BnMCA-Ia, BnMCA-IIa and BnMCA-IIi), an increase in MCA proteolytic activity and the activation of autophagy. Accordingly, inhibition of autophagy and MCA activity, either individually or in combination, suppressed cell death and increased the number of proembryos, indicating that both components play a pro-cell death role and account for decreased efficiency of early embryonic development. Therefore, MCAs and/or autophagy can be used as new biotechnological targets to improve in vitro embryogenesis in Brassica species and doubled-haploid plant production in crop breeding and propagation programs.
Keywords: Autophagy; Metacaspase; Microspore embryogenesis; Programmed cell death; Rapeseed; Stress.
� The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Japanese Society of Plant Physiologists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modulation of autophagy and protease activities by small bioactive compounds to reduce cell death and improve stress-induced microspore embryogenesis initiation in rapeseed and barley.Plant Signal Behav. 2019;14(2):1559577. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2018.1559577. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Plant Signal Behav. 2019. PMID: 30582408 Free PMC article.
-
Increase of histone acetylation by suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid enhances microspore reprogramming and expression of somatic embryogenesis transcription factors in Brassica napus.Plant Sci. 2025 Feb;351:112318. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2024.112318. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39577504
-
Arabinogalactan protein profiles and distribution patterns during microspore embryogenesis and pollen development in Brassica napus.Plant Reprod. 2013 Sep;26(3):231-43. doi: 10.1007/s00497-013-0217-8. Epub 2013 Jun 2. Plant Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23729197
-
Microspore embryogenesis: targeting the determinant factors of stress-induced cell reprogramming for crop improvement.J Exp Bot. 2019 Jun 1;70(11):2965-2978. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery464. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 30753698 Review.
-
Microspore embryogenesis in Brassica: calcium signaling, epigenetic modification, and programmed cell death.Planta. 2018 Dec;248(6):1339-1350. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-2996-5. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Planta. 2018. PMID: 30171331 Review.
Cited by
-
Autophagy-Mediated Regulation of Different Meristems in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 2;23(11):6236. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116236. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roads to Haploid Embryogenesis.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 5;12(2):243. doi: 10.3390/plants12020243. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microspore embryogenesis induction by mannitol and TSA results in a complex regulation of epigenetic dynamics and gene expression in bread wheat.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jan 9;13:1058421. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1058421. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36699843 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of microspore embryogenesis in bread wheat by mannitol pre-treatment is associated with the disruption of endogenous hormone balance and substantial accumulation of auxins.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Mar 22;25(1):370. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06389-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40119252 Free PMC article.
-
Brassica napus Haploid and Double Haploid Production and Its Latest Applications.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 May 18;45(5):4431-4450. doi: 10.3390/cimb45050282. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37232751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Avin-Wittenberg T. (2019) Autophagy and its role in plant abiotic stress management. Plant. Cell Environ. 42: 1045–1053. - PubMed
-
- Avin-Wittenberg T., Baluška F., Bozhkov P.V., Elander P.H., Fernie A.R., Galili G., et al. (2018) Autophagy-related approaches for improving nutrient use efficiency and crop yield protection. J. Exp. Bot. 69: 1335–1353. - PubMed
-
- B�r�ny I., Gonz�lez-Melendi P., Fad�n B., Mityk� J., Risue�o M.C., Testillano P.S. (2005) Microspore-derived embryogenesis in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.): Subcellular rearrangements through development. Biol. Cell 97: 709–722. - PubMed

