Traditional Herbal Medicines Against CNS Disorders from Bangladesh
- PMID: 33057963
- PMCID: PMC7648845
- DOI: 10.1007/s13659-020-00269-7
Traditional Herbal Medicines Against CNS Disorders from Bangladesh
Abstract
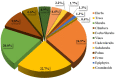
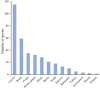
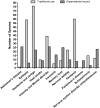
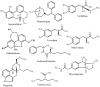
The majority of the population in Bangladesh uses traditional plant-based medicines to manage various ailments, including central nervous system (CNS) disorders. This review presents ethnobotanical information and relevant scientific studies on plants used in traditional healthcare for the management of various CNS disorders in Bangladesh. The information on the medicinal plants of Bangladesh effective against CNS disorders published in scientific journals, books, and reports was compiled from different electronic databases using specific key words. The present article provides comprehensive information on a total of 224 medicinal plant species belonging to 81 families used for the treatment of CNS disorders by the various peoples of Bangladesh. In total, we reviewed more than 290 relevant papers. In this study, leaves were found as the most often used plant organ, followed by roots, fruits, whole plants, barks, seeds, stems, rhizomes, and flowers. The Fabaceae family contributes the highest number of used species, followed by Rubiaceae, Lamiaceae, Cucurbitaceae, Vitaceae, Euphorbiaceae, Malvaceae, and Zingiberaceae. The most frequently used species (in decreasing order) are Asparagus racemosus, Centella asiatica, Stephania japonica, Aegle marmelos, Coccinia grandis, Tabernaemontana divaricata, Bacopa monnieri, Abroma augusta, and Scoparia dulcis. This review may serve as a starting point for a rational search for neuroactive natural products against CNS disorders within the Flora of Bangladesh.
Keywords: CNS disorder; Ethnopharmacology; Medicinal plants; Review; Traditional plants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ethnopharmacological survey of medicinal plants used by indigenous and tribal people in Rangamati, Bangladesh.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Dec 18;144(3):627-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.10.003. Epub 2012 Oct 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23064284
-
Medicinal plants for gastrointestinal diseases among the Kuki-Chin ethnolinguistic groups across Bangladesh, India, and Myanmar: A comparative and network analysis study.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Apr 6;251:112415. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112415. Epub 2020 Jan 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31917280 Review.
-
Ethnopharmacological survey of medicinal plants used by traditional health practitioners in Thanchi, Bandarban Hill Tracts, Bangladesh.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Aug 8;155(1):495-508. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.05.043. Epub 2014 Jun 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24892834
-
Ethnobotany of Medicinal Plants Used by Rakhine Indigenous Communities in Patuakhali and Barguna District of Southern Bangladesh.J Evid Based Integr Med. 2020 Jan-Dec;25:2515690X20971586. doi: 10.1177/2515690X20971586. J Evid Based Integr Med. 2020. PMID: 33356558 Free PMC article.
-
An overview on ethnobotanico-pharmacological studies carried out in Morocco, from 1991 to 2015: Systematic review (part 1).J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;267:113200. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113200. Epub 2020 Aug 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32750461
Cited by
-
Evaluation of cholinesterase inhibitory and antioxidant activity of Wedelia chinensis and isolation of apigenin as an active compound.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Jul 27;21(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03373-4. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 34315449 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Virtual Reality Technology in Clinical Practice, Teaching, and Research in Complementary and Alternative Medicine.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Aug 11;2022:1373170. doi: 10.1155/2022/1373170. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35990836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phyto-pharmacological Potential of Aegle marmelos (L.) for Neurological Disorders: Progress and Prospects.Recent Adv Food Nutr Agric. 2025;16(1):12-30. doi: 10.2174/012772574X289517240222045916. Recent Adv Food Nutr Agric. 2025. PMID: 38468524 Review.
-
Compounds from the Petroleum Ether Extract of Wedelia chinensis with Cytotoxic, Anticholinesterase, Antioxidant, and Antimicrobial Activities.Molecules. 2023 Jan 13;28(2):793. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020793. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677851 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional imaging of brains.Sci China Chem. 2023;66(2):324-366. doi: 10.1007/s11426-022-1408-5. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Sci China Chem. 2023. PMID: 36536633 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lakea S. UBCMJ. 2015;7:40–41.
-
- Kantati YT, Kodjo KM, Dogbeavou KS, Vaudry D, Leprince J, Gbeassor M. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016;181:214–220. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

