Deciphering the COVID-19 cytokine storm: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33058143
- PMCID: PMC7646004
- DOI: 10.1111/eci.13429
Deciphering the COVID-19 cytokine storm: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: The coronavirus pandemic has affected more than 20 million people so far. Elevated cytokines and suppressed immune responses have been hypothesized to set off a cytokine storm, contributing to ARDS, multiple-organ failure and, in the most severe cases, death. We aimed to quantify the differences in the circulating levels of major inflammatory and immunological markers between severe and nonsevere COVID-19 patients.
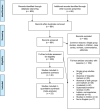
Methods: Relevant studies were identified from PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, SCOPUS and preprint servers. Risk of bias was assessed for each study, using appropriate checklists. All studies were described qualitatively and a subset was included in the meta-analysis, using forest plots.
Results: Based on 23 studies, mean cytokine levels were significantly higher (IL-6: MD, 19.55 pg/mL; CI, 14.80, 24.30; IL-8: MD, 19.18 pg/mL; CI, 2.94, 35.43; IL-10: MD, 3.66 pg/mL; CI, 2.41, 4.92; IL-2R: MD, 521.36 U/mL; CI, 87.15, 955.57; and TNF-alpha: MD, 1.11 pg/mL; CI, 0.07, 2.15) and T-lymphocyte levels were significantly lower (CD4+ T cells: MD, -165.28 cells/µL; CI, -207.58, -122.97; CD8+ T cells: MD, -106.51 cells/µL; CI, -128.59, -84.43) among severe cases as compared to nonsevere ones. There was heterogeneity across studies due to small sample sizes and nonuniformity in outcome assessment and varied definitions of disease severity. The overall quality of studies was sub-optimal.
Conclusion: Severe COVID-19 is characterized by significantly increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduced T lymphocytes. Well-designed and adequately powered prospective studies are needed to amplify the current evidence and provide definitive answers to dilemmas regarding timing and type of anti-COVID-19 therapy particularly in severe patients.
Keywords: CD4+ T cells; CD8+ T cells; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; cytokine storm; novel coronavirus.
© 2020 Stichting European Society for Clinical Investigation Journal Foundation. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Coronavirus COVID‐19 (2019‐nCoV) Dashboard by the CCSE at Johns Hopkins University [Internet]. https://gisanddata.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594.... Accessed June 16, 2020
-
- Henderson LA, Canna SW, Schulert GS, et al. On the Alert for Cytokine Storm: Immunopathology in COVID‐19. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/art.41285 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

