Generation of fully functional fluorescent fusion proteins to gain insights into ABCC6 biology
- PMID: 33058196
- PMCID: PMC7987643
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.13957
Generation of fully functional fluorescent fusion proteins to gain insights into ABCC6 biology
Abstract
ABCC6 mediates release of ATP from hepatocytes into the blood. Extracellularly, ATP is converted into the mineralization inhibitor pyrophosphate. Consequently, inactivating mutations in ABCC6 give low plasma pyrophosphate and underlie the ectopic mineralization disorder pseudoxanthoma elasticum. How ABCC6 mediates cellular ATP release is still unknown. Fluorescent ABCC6 fusion proteins would allow mechanistic studies, but fluorophores attached to the ABCC6 N- or C-terminus result in intracellular retention and degradation. Here we describe that intramolecular introduction of fluorophores yields fully functional ABCC6 fusion proteins. A corresponding ABCC6 variant in which the catalytic glutamate of the second nucleotide binding domain was mutated, correctly routed to the plasma membrane but was inactive. Finally, N-terminal His10 or FLAG tags did not affect activity of the fusion proteins, allowing their purification for biochemical characterization.
Keywords: ABC transporter; cellular ATP efflux; fluorescent fusion protein; pseudoxanthoma elasticum; purification.
© 2020 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
disclosure of conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

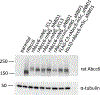

Similar articles
-
Mutagenic Analysis of the Putative ABCC6 Substrate-Binding Cavity Using a New Homology Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 27;22(13):6910. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136910. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34199119 Free PMC article.
-
ABCC6-mediated ATP secretion by the liver is the main source of the mineralization inhibitor inorganic pyrophosphate in the systemic circulation-brief report.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Sep;34(9):1985-9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304017. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24969777 Free PMC article.
-
ABCC6 prevents ectopic mineralization seen in pseudoxanthoma elasticum by inducing cellular nucleotide release.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Dec 10;110(50):20206-11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319582110. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24277820 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Functional Characterization of the ABCC6 Transporter in Hepatic Cells: Role on PXE, Cancer Therapy and Drug Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 11;22(6):2858. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062858. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33799762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From membrane to mineralization: the curious case of the ABCC6 transporter.FEBS Lett. 2020 Dec;594(23):4109-4133. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13981. Epub 2020 Nov 21. FEBS Lett. 2020. PMID: 33131056 Review.
Cited by
-
RAB10 Interacts with ABCB4 and Regulates Its Intracellular Traffic.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 30;22(13):7087. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137087. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34209301 Free PMC article.
-
CircZXDC Promotes Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Transdifferentiation via Regulating miRNA-125a-3p/ABCC6 in Moyamoya Disease.Cells. 2022 Nov 26;11(23):3792. doi: 10.3390/cells11233792. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497052 Free PMC article.
-
The Mineralization Regulator ANKH Mediates Cellular Efflux of ATP, Not Pyrophosphate.J Bone Miner Res. 2022 May;37(5):1024-1031. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4528. Epub 2022 Feb 28. J Bone Miner Res. 2022. PMID: 35147247 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence labeling strategies for cell surface expression of TRPV1.J Gen Physiol. 2024 Oct 7;156(10):e202313523. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202313523. Epub 2024 Aug 20. J Gen Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39162763 Free PMC article.
-
Detailed Phenotype Supports Pathogenicity of Hypomorphic Variant in ABCC6-Associated Pattern Dystrophy.Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2024 Jun 12;15(1):497-506. doi: 10.1159/000538045. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39015234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Le Saux O, Urban Z, Tschuch C, Csiszar K, Bacchelli B, Quaglino D, et al. Mutations in a Gene Encoding an ABC Transporter Cause Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum. Nature genetics. 2000;25(2). - PubMed
-
- Bergen AA, Plomp AS, Schuurman EJ, Terry S, Breuning M, Dauwerse H, et al. Mutations in ABCC6 Cause Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum. Nature genetics. 2000;25(2). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

