Infections in patients with lymphoproliferative diseases treated with targeted agents: SEIFEM multicentric retrospective study
- PMID: 33058237
- PMCID: PMC8246914
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.17145
Infections in patients with lymphoproliferative diseases treated with targeted agents: SEIFEM multicentric retrospective study
Abstract
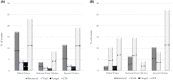
We describe the opportunistic infections occurring in 362 patients with lymphoproliferative disorders treated with ibrutinib and idelalisib in clinical practice. Overall, 108 of 362 patients (29·8%) developed infections, for a total of 152 events. Clinically defined infections (CDI) were 49·3% (75/152) and microbiologically defined infections (MDI) were 50·7% (77/152). Among 250 patients treated with ibrutinib, 28·8% (72/250) experienced one or more infections, for a total of 104 episodes. MDI were 49% (51/104). Bacterial infections were 66·7% (34/51), viral 19·6% (10/51) and invasive fungal diseases (IFD) 13·7% (7/51). Among the 112 patients treated with idelalisib, 32·1% (36/112) experienced one or more infections, for a total of 48 episodes. MDI were 54·2% (26/48). Bacterial infections were 34·6% (9/26), viral 61·5% (16/26) and IFD 3·8% (1/26). With ibrutinib, the rate of bacterial infections was significantly higher compared to idelalisib (66·7% vs. 34·6%; P = 0·007), while viral infections were most frequent in idelalisib (61·5% vs. 19·6%; P < 0·001). Although a higher rate of IFD was observed in patients treated with ibrutinib, the difference was not statistically significant (13·7% vs. 3·8% respectively; P = 0·18). Bacteria are the most frequent infections with ibrutinib, while viruses are most frequently involved with idelalisib.
Keywords: infections; lymphoproliferative diseases; targeted therapy.
© 2020 The Authors. British Journal of Haematology published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All other authors report no potential conflict.
Figures

References
-
- Morrison VA, Rai KR, Peterson BL, Kolitz JE, Elias L, Appelbaum FR, et al. Impact of therapy With chlorambucil, fludarabine, or fludarabine plus chlorambucil on infections in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Intergroup Study Cancer and Leukemia Group B 9011. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(16):3611–21. - PubMed
-
- Hensel M, Kornacker M, Yammeni S, Egerer G, Ho AD. Disease activity and pretreatment, rather than hypogammaglobulinaemia, are major risk factors for infectious complications in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2003;122(4):600–6. - PubMed
-
- Moreira J, Rabe KG, Cerhan JR, Kay NE, Wilson JW, Call TG, et al. Infectious complications among individuals with clinical monoclonal B‐cell lymphocytosis (MBL): a cohort study of newly diagnosed cases compared to controls. Leukemia. 2013;27(1):136–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

