MiR-590-3p regulates cardiomyocyte P19CL6 proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation in vitro by targeting PTPN1 via JNK/STAT/NF-kB pathway
- PMID: 33058302
- PMCID: PMC7691214
- DOI: 10.1111/iep.12377
MiR-590-3p regulates cardiomyocyte P19CL6 proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation in vitro by targeting PTPN1 via JNK/STAT/NF-kB pathway
Abstract
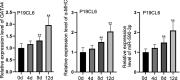
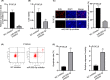
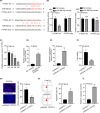
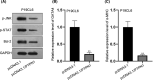
Cardiomyocyte differentiation is a multi-step process which involves a number of signalling pathways. microRNAs exhibit regulatory functions in various diseases and are involved in the signalling pathways in multiple physiological processes, but the specific functions of particular mRNAs is often not fully understood. of an example of this is that the role of miR-590-3p in the differentiation of cardiomyocytes remains unclear. In the current study, RT-qPCR was used to determine the expression of miR-590-3p in cardiomyocytes differentiated from the embryonic carcinoma cell line P19CL6. MTT, EdU, caspase-3 activity and flow cytometry assays were performed to examine the influence of miR-590-3p on cell behaviour. A luciferase assay was used to confirm binding between miR-590-3p and PTPN1. Western blotting was used to determine the relationship between the JNK/STAT/NF-kB pathway and PTPN1. The results inferred that miR-590-3p became heavily expressed in differentiated P19CL6. Knockdown miR-590-3p suppressed the cell proliferation while at the same time, accelerated apoptosis. Moreover, PTPN1 was identified as the target of miR-590-3p. More importantly, PTPN1 overexpression activated the JNK/STAT/NF-kB pathway and limited the differentiation of P19CL6. Thus the conclusions from this study are that miR-590-3p has the potential to regulate the proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation of cardiomyocyte P19CL6 in vitro by targeting PTPN1 via the JNK/STAT/NF-kB pathway.
Keywords: JNK; MiR-590-3p; NF-kB pathway; P19CL6; PTPN1; STAT.
© 2020 Company of the International Journal of Experimental Pathology (CIJEP).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors do not have anything to disclose and declare not conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-499 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis during late-stage cardiac differentiation via Sox6 and cyclin D1.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 11;8(9):e74504. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074504. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040263 Free PMC article.
-
miR-29b-3p suppresses the malignant biological behaviors of AML cells via inhibiting NF-κB and JAK/STAT signaling pathways by targeting HuR.BMC Cancer. 2022 Aug 20;22(1):909. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09996-1. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35986311 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-345-3p attenuates apoptosis and inflammation caused by oxidized low-density lipoprotein by targeting TRAF6 via TAK1/p38/NF-kB signaling in endothelial cells.Life Sci. 2020 Jan 15;241:117142. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117142. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31825793
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Prediction and analysis of microRNAs involved in COVID-19 inflammatory processes associated with the NF-kB and JAK/STAT signaling pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Nov;100:108071. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108071. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34482267 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circ_0124644 Serves as a ceRNA for miR-590-3p to Promote Hypoxia-Induced Cardiomyocytes Injury via Regulating SOX4.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 25;12:667724. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.667724. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34249089 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Age-Related MicroRNA Signature in Mesenchymal Stem Cells by using Computational Methods.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025;20(4):464-477. doi: 10.2174/011574888X291147240507072107. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 38747225
-
Preliminary investigation of the effect of ferulic acid on miRNAs and LncRNAs in Mongolian horse skeletal muscle satellite cells.Front Genet. 2025 Jul 18;16:1630614. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1630614. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40756204 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin alters distinct molecular pathways in breast cancer subtypes revealed by integrated miRNA/mRNA expression analysis.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022 Oct;5(10):e1596. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1596. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022. PMID: 34981672 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic alternative polyadenylation during iPSC differentiation into cardiomyocytes.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Oct 25;20:5859-5869. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.10.025. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36382196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takaya T, Nishi H, Horie T, Ono K, Hasegawa K. Roles of microRNAs and myocardial cell differentiation. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012;111:139‐152. - PubMed
-
- Hermeking H. MicroRNAs in the p53 network: micromanagement of tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:613‐626. - PubMed
-
- Adamopoulos PG, Tsiakanikas P, Scorilas A. Kallikrein‐related peptidases and associated microRNAs as promising prognostic biomarkers in gastrointestinal malignancies. Biol Chem. 2018;399:821‐836. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

