How bilayer properties influence membrane protein folding
- PMID: 33058341
- PMCID: PMC7679971
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3973
How bilayer properties influence membrane protein folding
Abstract
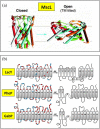
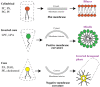
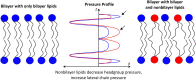
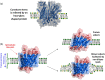
The question of how proteins manage to organize into a unique three-dimensional structure has been a major field of study since the first protein structures were determined. For membrane proteins, the question is made more complex because, unlike water-soluble proteins, the solvent is not homogenous or even unique. Each cell and organelle has a distinct lipid composition that can change in response to environmental stimuli. Thus, the study of membrane protein folding requires not only understanding how the unfolded chain navigates its way to the folded state, but also how changes in bilayer properties can affect that search. Here we review what we know so far about the impact of lipid composition on bilayer physical properties and how those properties can affect folding. A better understanding of the lipid bilayer and its effects on membrane protein folding is not only important for a theoretical understanding of the folding process, but can also have a practical impact on our ability to work with and design membrane proteins.
Keywords: lipids; membrane insertion; packing pressure; phospholipids; reconstitution; stability; topology.
© 2020 The Protein Society.
Conflict of interest statement
K.C. declares no conflict of interest. J.U.B. has founded a company involved in the production of natural chemicals that bears no direct relation to this work.
Figures

References
-
- Sohlenkamp C, Geiger O. Bacterial membrane lipids: Diversity in structures and pathways. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016;40:133–159. - PubMed
-
- Harayama T, Riezman H. Understanding the diversity of membrane lipid composition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19:281–296. - PubMed
-
- Shevchenko A, Simons K. Lipidomics: Coming to grips with lipid diversity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:593–598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

