The role of platelets in thrombus fibrosis and vessel wall remodeling after venous thrombosis
- PMID: 33058430
- PMCID: PMC8530247
- DOI: 10.1111/jth.15134
The role of platelets in thrombus fibrosis and vessel wall remodeling after venous thrombosis
Abstract
Purpose: Platelets are known to play an important role in venous thrombogenesis, but their role in thrombus maturation, resolution, and postthrombotic vein wall remodeling is unclear. The purpose of this study was to determine the role that circulating platelets play in the later phases of venous thrombosis.
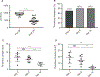
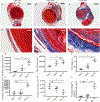
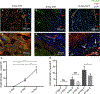
Methods: We used a murine inferior vena cava (IVC) stenosis model. Baseline studies in untreated mice were performed to determine an optimal postthrombotic time point for tissue harvest that would capture both thrombus maturation/resolution and postthrombotic vein wall remodeling. This time point was found to be postoperative day 10. After undergoing IVC ultrasound on day 2 to confirm venous thrombus formation, mice were treated with a daily injection of platelet-depleting antibody (anti-GP1bα) to maintain thrombocytopenia or with control IgG until postoperative day 10, at which time IVC and thrombi were harvested and thrombus length, volume, fibrosis, neovascularization, and smooth muscle cell invasion analyzed. Vein wall fibrosis and intimal thickening were also determined.
Results: Mice that were made thrombocytopenic after venous thrombogenesis had thrombi that were less fibrotic, with fewer invading smooth muscle cells. Furthermore, thrombocytopenia in the setting of venous thrombosis resulted in less postthrombotic vein wall intimal thickening. Thrombus volume did not differ between thrombocytopenic mice and their control peers.
Conclusions: This work suggests that circulating platelets contribute to venous thrombus maturation, fibrosis, and adverse vein wall remodeling, and that that inhibition of platelet recruitment may decrease thrombus and vein wall fibrosis, thus helping thrombolysis and preventing postthrombotic syndrome.
Keywords: fibrosis; platelets; post-thrombotic syndrome; vascular remodeling; venous thrombosis.
© 2020 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Dr. Wagner is on the Scientific Advisory Board of Neutrolis, a preclinical-stage biotech company focused on DNases. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pre-Clinical Model to Study Recurrent Venous Thrombosis in the Inferior Vena Cava.Thromb Haemost. 2018 Jun;118(6):1048-1057. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1645855. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Thromb Haemost. 2018. PMID: 29695021 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with an oral small molecule inhibitor of P selectin (PSI-697) decreases vein wall injury in a rat stenosis model of venous thrombosis.J Vasc Surg. 2006 Sep;44(3):625-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2006.05.021. J Vasc Surg. 2006. PMID: 16950445
-
The role of urokinase plasminogen activator and plasmin activator inhibitor-1 on vein wall remodeling in experimental deep vein thrombosis.J Vasc Surg. 2012 Oct;56(4):1089-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2012.02.054. Epub 2012 Jul 15. J Vasc Surg. 2012. PMID: 22796119 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of preoperative imaging prediction of renal cell carcinoma tumour thrombus inferior vena cava wall invasion.Clin Radiol. 2023 Jul;78(7):540-547. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2023.02.022. Epub 2023 Mar 25. Clin Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37085340
-
Critical review of mouse models of venous thrombosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Mar;32(3):556-62. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.244608. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22345593 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunothrombosis and the Role of Platelets in Venous Thromboembolic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 29;23(21):13176. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113176. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The application of neutrophil extracellular traps to thrombus age Estimation in rat deep vein thrombosis model.Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2025 Mar 20. doi: 10.1007/s12024-025-00986-w. Online ahead of print. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40111724
-
NET-(works) in arterial and venous thrombo-occlusive diseases.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 May 22;10:1155512. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1155512. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37283578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of platelet count in a murine stasis model of deep vein thrombosis.Platelets. 2024 Dec;35(1):2290916. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2023.2290916. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Platelets. 2024. PMID: 38099327
-
Early thrombus formation is required for eccentric and heterogeneous neointimal hyperplasia under disturbed flow.J Thromb Haemost. 2024 Dec;22(12):3614-3628. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2024.07.028. Epub 2024 Aug 21. J Thromb Haemost. 2024. PMID: 39173878
References
-
- Bartholomew JR. Update on the prevention of venous thromboembolism. Cleve Clin J Med. 2017;84:39–46. - PubMed
-
- Kearon C Natural history of venous thromboembolism. Circulation. 2003;107:22–31. - PubMed
-
- Goldhaber SZ, Buring JE, Lipnick RJ, Hennekens CH. Pooled analyses of randomized trials of streptokinase and heparin in phlebographically documented acute deep venous thrombosis. Am J Med. 1984;76:393–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

