DNA Damage Promotes Epithelial Hyperplasia and Fate Mis-specification via Fibroblast Inflammasome Activation
- PMID: 33058780
- PMCID: PMC7725994
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.09.021
DNA Damage Promotes Epithelial Hyperplasia and Fate Mis-specification via Fibroblast Inflammasome Activation
Abstract
DNA crosslinking agents are commonly used in cancer chemotherapy; however, responses of normal tissues to these agents have not been widely investigated. We reveal in mouse interfollicular epidermal, mammary and hair follicle epithelia that genotoxicity does not promote apoptosis but paradoxically induces hyperplasia and fate specification defects in quiescent stem cells. DNA damage to skin causes epithelial and dermal hyperplasia, tissue expansion, and proliferation-independent formation of abnormal K14/K10 dual-positive suprabasal cells. Unexpectedly, this behavior is epithelial cell non-autonomous and independent of an intact immune system. Instead, dermal fibroblasts are both necessary and sufficient to induce the epithelial response, which is mediated by activation of a fibroblast-specific NLRP3 inflammasome and subsequent IL-1β production. Thus, genotoxic agents that are used chemotherapeutically to promote cancer cell death can have the opposite effect on wild-type epithelia by inducing, via a non-autonomous IL-1β-driven mechanism, both hyperplasia and stem cell lineage defects.
Keywords: DNA damage; IL-1β; chemotherapy; epidermis; hair follicle; hyperplasia; inflammasome; lineage; mammary gland; stem cell.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
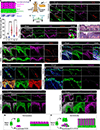

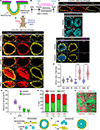
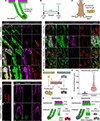
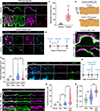

Comment in
-
Genotoxic Agents: An Unexpected Effect on Healthy Epithelia.Dev Cell. 2020 Dec 7;55(5):515-517. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.11.001. Dev Cell. 2020. PMID: 33290689
-
Commentary: DNA Damage Promotes Epithelial Hyperplasia and Fate Mis-specification via Fibroblast Inflammasome Activation.J Dermatol Skin Sci. 2022;4(2):24-28. doi: 10.29245/2767-5092/2022/2.1154. Epub 2022 Jun 28. J Dermatol Skin Sci. 2022. PMID: 36340857 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Non-canonical Inflammasome-Mediated IL-1β Production by Primary Endometrial Epithelial and Stromal Fibroblast Cells Is NLRP3 and Caspase-4 Dependent.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 5;10:102. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00102. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30804935 Free PMC article.
-
Genotoxic Agents: An Unexpected Effect on Healthy Epithelia.Dev Cell. 2020 Dec 7;55(5):515-517. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.11.001. Dev Cell. 2020. PMID: 33290689
-
Dengue Virus M Protein Promotes NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation To Induce Vascular Leakage in Mice.J Virol. 2019 Oct 15;93(21):e00996-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00996-19. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31413130 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 and NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathways are involved in Prototheca bovis infections of mouse mammary gland tissue and mammary epithelial cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 May 1;184:148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.04.005. Epub 2022 Apr 10. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35417750
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the Innate Immune Response to Gout.Immunol Invest. 2023 Apr;52(3):364-397. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2168554. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Immunol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36745138 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell Lineage Infidelity in PDAC Progression and Therapy Resistance.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Dec 2;9:795251. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.795251. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34926472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer as a Disease of Development Gone Awry.Annu Rev Pathol. 2024 Jan 24;19:397-421. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-031621-025610. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Annu Rev Pathol. 2024. PMID: 37832945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic Effects of LPS and MSU on NF-κB/NLRP3-mediated Inflammation in Fibroblast Cells.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Aug 8. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01865-5. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40779126 No abstract available.
-
The extracellular matrix fibulin 7 maintains epidermal stem cell heterogeneity during skin aging.EMBO Rep. 2022 Dec 6;23(12):e55478. doi: 10.15252/embr.202255478. Epub 2022 Oct 24. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 36278510 Free PMC article.
-
Commentary: DNA Damage Promotes Epithelial Hyperplasia and Fate Mis-specification via Fibroblast Inflammasome Activation.J Dermatol Skin Sci. 2022;4(2):24-28. doi: 10.29245/2767-5092/2022/2.1154. Epub 2022 Jun 28. J Dermatol Skin Sci. 2022. PMID: 36340857 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- BARRIENTOS S, STOJADINOVIC O, GOLINKO MS, BREM H & TOMIC-CANIC M 2008. Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen, 16, 585–601. - PubMed
-
- BLAAS L, PUCCI F, MESSAL HA, ANDERSSON AB, JOSUE RUIZ E, GERLING M, DOUAGI I, SPENCER-DENE B, MUSCH A, MITTER R, BHAW L, STONE R, BORNHORST D, SESAY AK, JONKERS J, STAMP G, MALANCHI I, TOFTGARD R & BEHRENS A 2016. Lgr6 labels a rare population of mammary gland progenitor cells that are able to originate luminal mammary tumours. Nat Cell Biol, 18, 1346–1356. - PMC - PubMed
-
- CHEN X, WU Y, DONG H, ZHANG CY & ZHANG Y 2013. Platinum-Based Agents for Individualized Cancer Treatment. Current Molecular Medicine, 13, 1603–1612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

