Usefulness of Elevated Troponin to Predict Death in Patients With COVID-19 and Myocardial Injury
- PMID: 33058800
- PMCID: PMC7550867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.09.060
Usefulness of Elevated Troponin to Predict Death in Patients With COVID-19 and Myocardial Injury
Abstract
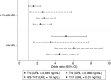
Elevations in troponin levels have been shown to predict mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The role of inflammation in myocardial injury remains unclear. We sought to determine the association of elevated troponin with mortality in a large, ethnically diverse population of patients hospitalized with COVID-19, and to determine the association of elevated inflammatory markers with increased troponin levels. We reviewed all patients admitted at our health system with COVID-19 from March 1 to April 27, 2020, who had a troponin assessment within 48 hours of admission. We used logistic regression to calculate odds ratios (ORs) for mortality during hospitalization, controlling for demographics, co-morbidities, and markers of inflammation. Of 11,159 patients hospitalized with COVID-19, 6,247 had a troponin assessment within 48 hours. Of these, 4,426 (71%) patients had normal, 919 (15%) had mildly elevated, and 902 (14%) had severely elevated troponin. Acute phase and inflammatory markers were significantly elevated in patients with mildly and severely elevated troponin compared with normal troponin. Patients with elevated troponin had significantly increased odds of death for mildly elevated compared with normal troponin (adjusted OR, 2.06; 95% confidence interval, 1.68 to 2.53; p < 0.001) and for severely elevated compared with normal troponin (OR, 4.51; 95% confidence interval, 3.66 to 5.54; p < 0.001) independently of elevation in inflammatory markers. In conclusion, patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and elevated troponin had markedly increased mortality compared with patients with normal troponin levels. This risk was independent of cardiovascular co-morbidities and elevated markers of inflammation.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Lala A, Johnson KW, Januzzi JL, Russak AJ, Paranjpe I, Richter F, Zhao S, Somani S, Van Vleck T, Vaid A, Chaudhry F, De Freitas JK, Fayad ZA, Pinney SP, Levin M, Charney A, Bagiella E, Narula J, Glicksberg BS, Nadkarni G, Mancini DM, Fuster V, Mount Sinai Covid Informatics C Prevalence and impact of myocardial injury in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 [Epub ahead of print] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497–506. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

