In situ immunization of a TLR9 agonist virus-like particle enhances anti-PD1 therapy
- PMID: 33060147
- PMCID: PMC7566437
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000940
In situ immunization of a TLR9 agonist virus-like particle enhances anti-PD1 therapy
Abstract
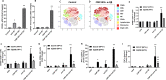
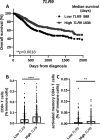
Background: CMP-001 is a novel Toll-like receptor-9 agonist that consists of an unmethylated CpG-A motif-rich G10 oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) encapsulated in virus-like particles. In situ vaccination of CMP-001 is believed to activate local tumor-associated plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) leading to type I interferon secretion and tumor antigen presentation to T cells and systemic antitumor T cell responses. This study is designed to investigate if CMP-001 would enhance head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) tumor response to anti-programmed cell death protein-1 (anti-PD-1) therapy in a human papilloma virus-positive (HPV+) tumor mouse model.
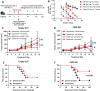
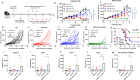
Methods: Immune cell activation in response to CMP-001±anti-Qβ was performed using co-cultures of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and HPV+/HPV- HNSCC cells and then analyzed by flow cytometry. In situ vaccination with CMP-001 alone and in combination with anti-PD-1 was investigated in C57BL/6 mice-bearing mEERL HNSCC tumors and analyzed for anti-Qβ development, antitumor response, survival and immune cell recruitment. The role of antitumor immune response due to CMP-001+anti-PD-1 treatment was investigated by the depletion of natural killer (NK), CD4+ T, and CD8+ T cells.
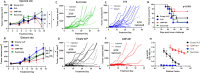
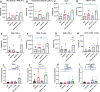
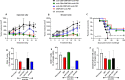
Results: Results showed that the activity of CMP-001 on immune cell (pDCs, monocytes, CD4+/CD8+ T cells and NK cells) activation depends on the presence of anti-Qβ. A 2-week 'priming' period after subcutaneous administration of CMP-001 was required for robust anti-Qβ development in mice. In situ vaccination of CMP-001 was superior to unencapsulated G10 CpG-A ODN at suppressing both injected and uninjected (distant) tumors. In situ vaccination of CMP-001 in combination with anti-PD-1 therapy induced durable tumor regression at injected and distant tumors and significantly prolonged mouse survival compared with anti-PD-1 therapy alone. The antitumor effect of CMP-001+anti-PD-1 was accompanied by increased interferon gamma (IFNγ)+ CD4+/CD8+ T cells compared with control-treated mice. The therapeutic and abscopal effect of CMP-001+ anti-PD-1 therapy was completely abrogated by CD8+ T cell depletion.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate that in situ vaccination with CMP-001 can induce both local and abscopal antitumor immune responses. Additionally, the antitumor efficacy of CMP-001 combined with α-PD-1 therapy warrants further study as a novel immunotherapeutic strategy for the treatment of HNSCC.
Keywords: adjuvants; dendritic cells; head and neck neoplasms; immunologic; immunotherapy; vaccination.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibody Opsonization of a TLR9 Agonist-Containing Virus-like Particle Enhances In Situ Immunization.J Immunol. 2020 Mar 1;204(5):1386-1394. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900742. Epub 2020 Jan 17. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31953355 Free PMC article.
-
Direct and indirect immune effects of CMP-001, a virus-like particle containing a TLR9 agonist.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jun;9(6):e002484. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002484. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34083419 Free PMC article.
-
Discrepant antitumor efficacies of three CpG oligodeoxynucleotide classes in monotherapy and co-therapy with PD-1 blockade.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Nov;161:105293. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105293. Epub 2020 Nov 8. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 33176206
-
Programmed Death-1/Programmed Death-Ligand 1-Axis Blockade in Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stratified by Human Papillomavirus Status: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 7;12:645170. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.645170. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33897693 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy for HPV negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024 Sep;1879(5):189138. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189138. Epub 2024 Jun 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38889878 Review.
Cited by
-
In situ treatment with a TLR9 agonist virus-like particle to promote immune responses against oral epithelial dysplasia progression.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025 May 3;74(6):189. doi: 10.1007/s00262-025-04023-1. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40317310 Free PMC article.
-
CpG Oligodeoxynucleotides for Anticancer Monotherapy from Preclinical Stages to Clinical Trials.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 28;14(1):73. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010073. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 35056969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering Therapeutic Strategies in Cancer Immunotherapy via Exogenous Delivery of Toll-like Receptor Agonists.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Aug 31;13(9):1374. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091374. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lefitolimod in Combination with Ipilimumab in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors: A Phase I Trial.J Immunother Precis Oncol. 2025 Feb 7;8(2):89-98. doi: 10.36401/JIPO-24-17. eCollection 2025 May. J Immunother Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39959251 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells in Gastric Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 3;12:818314. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.818314. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35311157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R, et al. . KEYNOTE-048: phase III study of first-line pembrolizumab (P) for recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (r/m HNSCC). Ann Oncol 2018;29:viii729 10.1093/annonc/mdy424.045 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
