Comparative host-coronavirus protein interaction networks reveal pan-viral disease mechanisms
- PMID: 33060197
- PMCID: PMC7808408
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abe9403
Comparative host-coronavirus protein interaction networks reveal pan-viral disease mechanisms
Abstract
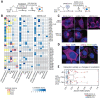
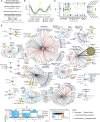
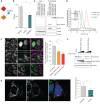
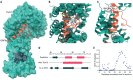
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is a grave threat to public health and the global economy. SARS-CoV-2 is closely related to the more lethal but less transmissible coronaviruses SARS-CoV-1 and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). Here, we have carried out comparative viral-human protein-protein interaction and viral protein localization analyses for all three viruses. Subsequent functional genetic screening identified host factors that functionally impinge on coronavirus proliferation, including Tom70, a mitochondrial chaperone protein that interacts with both SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 ORF9b, an interaction we structurally characterized using cryo-electron microscopy. Combining genetically validated host factors with both COVID-19 patient genetic data and medical billing records identified molecular mechanisms and potential drug treatments that merit further molecular and clinical study.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures





Comment in
-
Conserved host-pathogen interactions identify novel treatment options in betacoronavirus infections.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Feb 10;6(1):57. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00480-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33563888 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Olanzapine, risperidone and quetiapine: Do these atypical antipsychotics have a protective effect for SARS-CoV-2?Schizophr Res. 2022 Mar;241:140-141. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2022.01.035. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Schizophr Res. 2022. PMID: 35123336 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Beigel J. H., Tomashek K. M., Dodd L. E., Mehta A. K., Zingman B. S., Kalil A. C., Hohmann E., Chu H. Y., Luetkemeyer A., Kline S., Lopez de Castilla D., Finberg R. W., Dierberg K., Tapson V., Hsieh L., Patterson T. F., Paredes R., Sweeney D. A., Short W. R., Touloumi G., Lye D. C., Ohmagari N., Oh M.-d., Ruiz-Palacios G. M., Benfield T., Fätkenheuer G., Kortepeter M. G., Atmar R. L., Creech C. B., Lundgren J., Babiker A. G., Pett S., Neaton J. D., Burgess T. H., Bonnett T., Green M., Makowski M., Osinusi A., Nayak S., Lane H. C., ACTT-1 Study Group Members , Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—Final report. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 1813–1826 (2020). 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gordon D. E., Jang G. M., Bouhaddou M., Xu J., Obernier K., White K. M., O’Meara M. J., Rezelj V. V., Guo J. Z., Swaney D. L., Tummino T. A., Hüttenhain R., Kaake R. M., Richards A. L., Tutuncuoglu B., Foussard H., Batra J., Haas K., Modak M., Kim M., Haas P., Polacco B. J., Braberg H., Fabius J. M., Eckhardt M., Soucheray M., Bennett M. J., Cakir M., McGregor M. J., Li Q., Meyer B., Roesch F., Vallet T., Mac Kain A., Miorin L., Moreno E., Naing Z. Z. C., Zhou Y., Peng S., Shi Y., Zhang Z., Shen W., Kirby I. T., Melnyk J. E., Chorba J. S., Lou K., Dai S. A., Barrio-Hernandez I., Memon D., Hernandez-Armenta C., Lyu J., Mathy C. J. P., Perica T., Pilla K. B., Ganesan S. J., Saltzberg D. J., Rakesh R., Liu X., Rosenthal S. B., Calviello L., Venkataramanan S., Liboy-Lugo J., Lin Y., Huang X.-P., Liu Y., Wankowicz S. A., Bohn M., Safari M., Ugur F. S., Koh C., Savar N. S., Tran Q. D., Shengjuler D., Fletcher S. J., O’Neal M. C., Cai Y., Chang J. C. J., Broadhurst D. J., Klippsten S., Sharp P. P., Wenzell N. A., Kuzuoglu-Ozturk D., Wang H.-Y., Trenker R., Young J. M., Cavero D. A., Hiatt J., Roth T. L., Rathore U., Subramanian A., Noack J., Hubert M., Stroud R. M., Frankel A. D., Rosenberg O. S., Verba K. A., Agard D. A., Ott M., Emerman M., Jura N., von Zastrow M., Verdin E., Ashworth A., Schwartz O., d’Enfert C., Mukherjee S., Jacobson M., Malik H. S., Fujimori D. G., Ideker T., Craik C. S., Floor S. N., Fraser J. S., Gross J. D., Sali A., Roth B. L., Ruggero D., Taunton J., Kortemme T., Beltrao P., Vignuzzi M., García-Sastre A., Shokat K. M., Shoichet B. K., Krogan N. J., A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 583, 459–468 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM024485/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI060537/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG008742/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI122747/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA239333/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/V03541X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AI128214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM122481/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12016/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U19 AI135972/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI063302/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- BB/J014443/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN272201400008C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AI143401/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI120694/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008284/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- U19 AI135990/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM137463/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 201366/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 NS089713/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM118099/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_19026/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HG009979/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI120943/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_00018/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 AI150476/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12014/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K99 GM138753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA239336/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI143292/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

