Mesenchymal stem cells reverse EMT process through blocking the activation of NF-κB and Hedgehog pathways in LPS-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 33060560
- PMCID: PMC7567061
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-03034-3
Mesenchymal stem cells reverse EMT process through blocking the activation of NF-κB and Hedgehog pathways in LPS-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
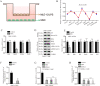
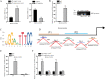
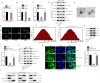
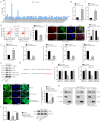
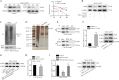
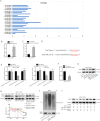
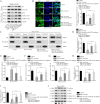
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a pulmonary disorder, which can result in fibrosis of the lung tissues. Recently, mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) has become a novel therapeutic method for ALI. However, the potential mechanism by which MSC regulates the progression of ALI remains blurry. The present study focused on investigating the mechanism underneath MSC-reversed lung injury and fibrosis. At first, we determined that coculture with MSC led to the inactivation of NF-κB signaling and therefore suppressed hedgehog pathway in LPS-treated MLE-12 cells. Besides, we confirmed that MSC-exosomes were responsible for the inhibition of EMT process in LPS-treated MLE-12 cells through transmitting miRNAs. Mechanism investigation revealed that MSC-exosome transmitted miR-182-5p and miR-23a-3p into LPS-treated MLE-12 cells to, respectively, target Ikbkb and Usp5. Of note, Usp5 interacted with IKKβ to hamper IKKβ ubiquitination. Moreover, co-inhibition of miR-182-5p and miR-23a-3p offset the suppression of MSC on EMT process in LPS-treated MLE-12 cells as well as in LPS-injured lungs of mice. Besides, the retarding effect of MSC on p65 nuclear translocation was also counteracted after co-inhibiting miR-182-5p and miR-23a-3p, both in vitro and in vivo. In summary, MSC-exosome transmitted miR-23a-3p and miR-182-5p reversed the progression of LPS-induced lung injury and fibrosis through inhibiting NF-κB and hedgehog pathways via silencing Ikbkb and destabilizing IKKβ.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

