Retinal involvement and ocular findings in COVID-19 pneumonia patients
- PMID: 33060700
- PMCID: PMC7566835
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-74446-6
Retinal involvement and ocular findings in COVID-19 pneumonia patients
Abstract
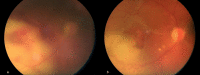
Changes in immune and coagulation systems and possible viral spread through the blood-brain barrier have been described in SARS-CoV-2 infection. In this study, we evaluated the possible retinal involvement and ocular findings in severe COVID-19 pneumonia patients. A cross-sectional study was conducted on 46 patients affected by severe COVID-19 who were hospitalized in one intensive care unit (ICU) and in two infectious disease wards, including bedside eye screening, corneal sensitivity assessment and retinography. A total of 43 SARS-CoV-2-positive pneumonia patients affected with COVID-19 pneumonia were included, including 25 males and 18 females, with a median age of 70 years [IQR 59-78]. Except for one patient with unilateral posterior chorioretinitis of opportunistic origin, of whom aqueous tap was negative for SARS-CoV-2, no further retinal manifestation related to COVID-19 infection was found in our cohort. We found 3 patients (7%) with bilateral conjunctivitis in whom PCR analysis on conjunctival swabs provided negative results for SARS-CoV-2. No alterations in corneal sensitivity were found. We demonstrated the absence of retinal involvement in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia patients. Ophthalmologic evaluation in COVID-19, particularly in patients hospitalized in an ICU setting, may be useful to reveal systemic co-infections by opportunistic pathogens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Nuovo Coronarivirus. Ministero della Salutehttps://www.salute.gov.it/nuovocoronavirus. Accessed 5 June 2020 (2020).
-
- Carod-Artal FJ. Neurological complications of coronavirus and COVID-19. Rev. Neurol. 2020;70(9):311–322. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

