An unusual combination of discreet subaortic membrane, aortopulmonary window, severe aortic insufficiency and rheumatic mitral regurgitation
- PMID: 33060900
- PMCID: PMC7523598
- DOI: 10.1007/s12055-017-0589-8
An unusual combination of discreet subaortic membrane, aortopulmonary window, severe aortic insufficiency and rheumatic mitral regurgitation
Abstract
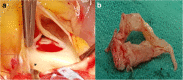
We report a 15-year-old female patient with an unusual combination of discreet subaortic membrane, aortopulmonary window, severe aortic insufficiency and rheumatic mitral regurgitation.
Keywords: Aortopulmonary window; Rheumatic heart disease; Subaortic membrane.
© Indian Association of Cardiovascular-Thoracic Surgeons 2017.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Adult case of aortopulmonary window with aortic regurgitation: a case report].Kokyu To Junkan. 1993 Nov;41(11):1113-5. Kokyu To Junkan. 1993. PMID: 8256054 Japanese.
-
Transesophageal echocardiographic recognition of subaortic complications in aortic valve endocarditis. Clinical and surgical implications.Circulation. 1992 Aug;86(2):353-62. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.2.353. Circulation. 1992. PMID: 1638704
-
Surgical management of aortopulmonary window.Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000 Sep;48(9):557-61. doi: 10.1007/BF03218200. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000. PMID: 11030126
-
Current status of surgery for rheumatic carditis in children.Ann Thorac Surg. 2004 Oct;78(4):1403-8. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.04.079. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004. PMID: 15464505 Review.
-
Morphologic features of the normal and abnormal mitral valve.Am J Cardiol. 1983 Mar 15;51(6):1005-28. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(83)80181-7. Am J Cardiol. 1983. PMID: 6338691 Review.
Cited by
-
Subaortic membrane in adult patients: retrospective study of clinical characteristics, outcomes, and echocardiographic associations and review of literature.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2025 Aug 7. doi: 10.1007/s10554-025-03489-5. Online ahead of print. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40773030
References
-
- Tefera E, Gedlu E, Bezabih A, et al. Outcome in children operated for membranous subaortic stenosis: membrane resection plus aggressive septal myectomy versus membrane resection alone. World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg. 2015;6:424–8. - PubMed
-
- Talwar S, Siddharth B, Gupta SK, et al. Aortopulmonary window: results of repair beyond infancy. Interact CardioVasc Thorac Surg. 2017; doi:10.1093/icvts/ivx/158. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
