Monocytes enhance the inflammatory response to TLR2 stimulation in aortic valve interstitial cells through paracrine up-regulation of TLR2 level
- PMID: 33061818
- PMCID: PMC7545700
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.49332
Monocytes enhance the inflammatory response to TLR2 stimulation in aortic valve interstitial cells through paracrine up-regulation of TLR2 level
Abstract
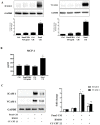
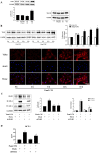
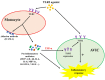
Background and Objectives: Chronic valvular inflammation associated with monocyte infiltration promotes calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) progression. Further, innate immunity in aortic valve interstitial cells (AVICs), mediated by Toll-like receptors (TLRs), up-regulates cellular inflammatory, fibrogenic and osteogenic activities. Currently, the pro-inflammatory communication between monocytes and AVICs and the underlying mechanism are unclear. We hypothesized that monocytes up-regulate AVIC inflammatory activity. This study sought to characterize the interaction between monocytes and AVICs and to elucidate the mechanism underlying cell-to-cell communication. Methods and Results: AVICs, monocytes and co-cultures were exposed to a low concentration of TLR2 activator Pam3CSK4 (0.03 µg/ml). The TLR2 activator at this dose induced a marked increase in AVIC production of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 only when co-cultured with monocytes. Adding conditioned medium from Pam3CSK4-treated monocytes (Pam3 CM, containing 0.1 µg/ml of Pam3CSK4) to AVIC culture (30% vol/vol; diluting Pam3CSK4 to 0.03 µg/ml) greatly increased the expression of adhesion molecules while adding conditioned medium from untreated monocytes (control CM) had no effect. Inhibition or knockdown of TLR2 in AVICs markedly reduced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression induced by Pam3 CM. Further, Pam3 CM increased TLR2 levels in AVICs. Multiplex-ELISA analysis of Pam3 CM identified greater levels of TNF-α. Neutralization of TNF-α abolished the effect of Pam3 CM on AVIC TLR2 levels, resulting in marked attenuation of its potency in the induction of adhesion molecule expression. Conclusions: This study demonstrates that activated monocytes use paracrine signaling to sensitize AVICs for inflammatory responses to a low level of TLR2 activator. The mechanism of sensitization involves up-regulation of AVIC TLR2 levels by TNF-α from monocytes. Infiltrated monocytes in aortic valve tissue may exacerbate valvular inflammation by rendering AVICs hypersensitive to TLR2 activators.
Keywords: Aortic valves; Toll-like receptor; adhesion molecules; inflammation; monocytes.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pro-inflammatory mediators released by activated monocytes promote aortic valve fibrocalcific activity.Mol Med. 2022 Jan 21;28(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00433-4. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35062861 Free PMC article.
-
Monocytes augment inflammatory responses in human aortic valve interstitial cells via β2-integrin/ICAM-1-mediated signaling.Inflamm Res. 2022 Jun;71(5-6):681-694. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01566-2. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35411432 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4 Stimulation Promotes Human AVIC Fibrogenic Activity through Upregulation of Neurotrophin 3 Production.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 14;21(4):1276. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041276. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32074942 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-osteogenic phenotype of human aortic valve interstitial cells is associated with higher levels of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 and enhanced expression of bone morphogenetic protein 2.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009 Feb 10;53(6):491-500. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.09.052. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 19195606
-
Soluble biglycan induces the production of ICAM-1 and MCP-1 in human aortic valve interstitial cells through TLR2/4 and the ERK1/2 pathway.Inflamm Res. 2014 Sep;63(9):703-10. doi: 10.1007/s00011-014-0743-3. Epub 2014 May 30. Inflamm Res. 2014. PMID: 24875140 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Adjustment of the Framingham index by abdominal aortic calcification scores enables a more accurate prediction of long-term cardiac events in general population aged 40 years and above: evidence from NHANES 2013-2014.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jan 14;25(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21383-6. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39810136 Free PMC article.
-
Saponins of Paris polyphylla for the Improvement of Acne: Anti-Inflammatory, Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Immunomodulatory Effects.Molecules. 2024 Apr 15;29(8):1793. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081793. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro-inflammatory mediators released by activated monocytes promote aortic valve fibrocalcific activity.Mol Med. 2022 Jan 21;28(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00433-4. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35062861 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease: Paracrine and Juxtacrine Disease Drivers.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 2;14(12):1547. doi: 10.3390/biom14121547. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monocytes augment inflammatory responses in human aortic valve interstitial cells via β2-integrin/ICAM-1-mediated signaling.Inflamm Res. 2022 Jun;71(5-6):681-694. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01566-2. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35411432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Freeman RV, Otto CM. Spectrum of calcific aortic valve disease: pathogenesis, disease progression, and treatment strategies. Circulation. 2005;111:3316–26. - PubMed
-
- Cote N, Mahmut A, Bosse Y. et al. Inflammation is associated with the remodeling of calcific aortic valve disease. Inflammation. 2013;36:573–81. - PubMed
-
- Furukawa K. Recent advances in research on human aortic valve calcification. J Pharmacol Sci. 2014;124:129–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

