LOXL1-AS1 contributes to the proliferation and migration of laryngocarcinoma cells through miR-589-5p/TRAF6 axis
- PMID: 33061856
- PMCID: PMC7552551
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-020-01565-5
LOXL1-AS1 contributes to the proliferation and migration of laryngocarcinoma cells through miR-589-5p/TRAF6 axis
Abstract
Background: LOXL1-AS1 is a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) that plays crucial roles in various cancers. However, the functional role of LOXL1-AS1 in laryngocarcinoma remains unclear. Thus we planned to probe into the function and underlying mechanism of LOXL1-AS1 in laryngocarcinoma.
Methods: Gene expression was evaluated in laryngocarcinoma cells using RT-qPCR. The ability of cell proliferation and migration was assessed by CCK8, colony formation, wound healing and transwell assays. The interaction among LOXL1-AS1, miR-589-5p and TRAF6 was detected by Ago2-RIP, RNA pull down and luciferase reporter assays.
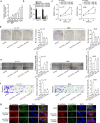
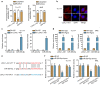
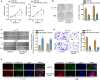
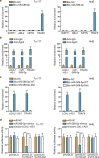
Results: LOXL1-AS1 was overexpressed in laryngocarcinoma cells. Silencing of LOXL1-AS1 suppressed cell proliferation, migration and EMT in laryngocarcinoma. Moreover, miR-589-5p, the downstream of LOXL1-AS1, directly targeted TRAF6 in laryngocarcinoma. Importantly, LOXL1-AS1 augmented TRAF6 expression in laryngocarcinoma cells by sequestering miR-589-5p. Besides, miR-589-5p worked as a tumor-inhibitor while TRAF6 functioned as a tumor-facilitator in laryngocarcinoma. Of note, rescue experiments both in vitro and in vivo validated that LOXL1-AS1 aggravated the malignancy in laryngocarcinoma by targeting miR-589-5p/TRAF6 pathway.
Conclusions: LOXL1-AS1 promotes the proliferation and migration of laryngocarcinoma cells through absorbing miR-589-5p to upregulate TRAF6 expression.
Keywords: LOXL1-AS1; Laryngocarcinoma; TRAF6; miR-589-5p.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Huo X, Han S, Wu G, Latchoumanin O, Zhou G, Hebbard L, George J, Qiao L. Dysregulated long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in hepatocellular carcinoma: implications for tumorigenesis, disease progression, and liver cancer stem cells. Mol Cancer. 2017;16(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0734-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

