Afferent and Efferent Visual Markers of Alzheimer's Disease: A Review and Update in Early Stage Disease
- PMID: 33061906
- PMCID: PMC7518395
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.572337
Afferent and Efferent Visual Markers of Alzheimer's Disease: A Review and Update in Early Stage Disease
Abstract
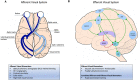
Vision, which requires extensive neural involvement, is often impaired in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Over the last few decades, accumulating evidence has shown that various visual functions and structures are compromised in Alzheimer's dementia and when measured can detect those with dementia from those with normal aging. These visual changes involve both the afferent and efferent parts of the visual system, which correspond to the sensory and eye movement aspects of vision, respectively. There are fewer, but a growing number of studies, that focus on the detection of predementia stages. Visual biomarkers that detect these stages are paramount in the development of successful disease-modifying therapies by identifying appropriate research participants and in identifying those who would receive future therapies. This review provides a summary and update on common afferent and efferent visual markers of AD with a focus on mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and preclinical disease detection. We further propose future directions in this area. Given the ease of performing visual tests, the accessibility of the eye, and advances in ocular technology, visual measures have the potential to be effective, practical, and non-invasive biomarkers of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; afferent visual system; efferent visual system; mild cognitive impairment; optical coherence tomography; pupillometry; saccadic eye movement; visual biomarkers.
Copyright © 2020 Wu, Masurkar and Balcer.
Figures
References
-
- Albert M. S., DeKosky S. T., Dickson D., Dubois B., Feldman H. H., Fox N. C., et al. (2011). The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the national institute on aging-Alzheimer’s association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 7, 270–279. 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Almeida A. L. M., Pires L. A., Figueiredo E. A., Costa-Cunha L. V. F., Zacharias L. C., Preti R. C., et al. (2019). Correlation between cognitive impairment and retinal neural loss assessed by swept-source optical coherence tomography in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimers Dement. 11, 659–669. 10.1016/j.dadm.2019.08.006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures (2019). Alzheimer’s Association. Available online at: www.alz.org/facts/. Accessed April 9, 2019.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

