Comprehensive Analysis of Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homologs (Rboh) Gene Family and Function of GbRboh5/18 on Verticillium Wilt Resistance in Gossypium barbadense
- PMID: 33061930
- PMCID: PMC7517705
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00788
Comprehensive Analysis of Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homologs (Rboh) Gene Family and Function of GbRboh5/18 on Verticillium Wilt Resistance in Gossypium barbadense
Abstract
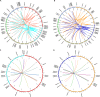
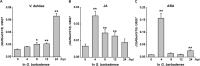
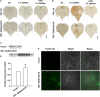
Respiratory burst oxidase homologs (Rbohs) play a predominant role in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, which is crucial in plant growth, differentiation, as well as their responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. To date, however, there is little knowledge about the function of cotton Rboh genes. Here, we identified a total of 87 Rbohs from five sequenced Gossypium species (the diploids Gossypium arboreum, Gossypium raimondii, and Gossypium australe, and the allotetraploids Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense) via BLAST searching their genomes. Phylogenetic analysis of the putative 87 cotton Rbohs revealed that they were divided into seven clades. All members within the same clade are generally similar to each other in terms of gene structure and conserved domain arrangement. In G. barbadense, the expression levels of GbRbohs in the CladeD were induced in response to a fungal pathogen and to hormones (i.e., jasmonic acid and abscisic acid), based upon which the main functional member in CladeD was discerned to be GbRboh5/18. Further functional and physiological analyses showed that the knock-down of GbRboh5/18 expression attenuates plant resistance to Verticillium dahliae infection. Combined with the molecular and biochemical analyses, we found less ROS accumulation in GbRboh5/18-VIGS plants than in control plants after V. dahliae infection. Overexpression of GbRboh5/18 in G. barbadense resulted in more ROS accumulation than in control plants. These results suggest that GbRboh5/18 enhances the cotton plants' resistance against V. dahliae by elevating the levels of ROS accumulation. By integrating phylogenetic, molecular, and biochemical approaches, this comprehensive study provides a detailed overview of the number, phylogeny, and evolution of the Rboh gene family from five sequenced Gossypium species, as well as elucidating the function of GbRboh5/18 for plant resistance against V. dahliae. This study sheds fresh light on the molecular evolutionary properties and function of Rboh genes in cotton, and provides a reference for improving cotton's responses to the pathogen V. dahliae.
Keywords: GbRboh5/18; Gossypium; V. dahliae; reactive oxygen species (ROS); respiratory burst oxidase homologs (Rbohs).
Copyright © 2020 Chang, Li, Shi, Geng, Geng, Liu, Zhang and Cai.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homolog Protein D (GhRbohD) Positively Regulates the Cotton Resistance to Verticillium dahliae.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 2;22(23):13041. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313041. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884844 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and expression analysis of arabinogalactan protein genes in cotton reveal the function of GhAGP15 in Verticillium dahliae resistance.Gene. 2022 May 15;822:146336. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146336. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35182675
-
Evolutionary and Characteristic Analysis of RING-DUF1117 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Genes in Gossypium Discerning the Role of GhRDUF4D in Verticillium dahliae Resistance.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 3;11(8):1145. doi: 10.3390/biom11081145. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439811 Free PMC article.
-
Insights to Gossypium defense response against Verticillium dahliae: the Cotton Cancer.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 May 1;23(2):142. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-01065-5. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37121989 Review.
-
Orchestrating ROS regulation: coordinated post-translational modification switches in NADPH oxidases.New Phytol. 2025 Jan;245(2):510-522. doi: 10.1111/nph.20231. Epub 2024 Oct 29. New Phytol. 2025. PMID: 39468860 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide analysis of respiratory burst oxidase homolog gene family in pea (Pisum sativum L.).Front Plant Sci. 2023 Dec 12;14:1321952. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1321952. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 38155848 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homolog (Rboh) Family Genes From Pyropia yezoensis and Their Correlation With Archeospore Release.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jul 12;13:929299. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.929299. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35903222 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification, Classification, Expression Analysis, and Screening of Drought and Heat Resistance-Related Candidates of the Rboh Gene Family in Wheat.Plants (Basel). 2024 Nov 30;13(23):3377. doi: 10.3390/plants13233377. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39683170 Free PMC article.
-
Sugarcane responses to two strains of Xanthomonas albilineans differing in pathogenicity through a differential modulation of salicylic acid and reactive oxygen species.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Dec 15;13:1087525. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1087525. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36589125 Free PMC article.
-
The Characteristics and Expression Analysis of the Tomato SlRBOH Gene Family under Exogenous Phytohormone Treatments and Abiotic Stresses.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 26;25(11):5780. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115780. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891968 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

