Artificial Intelligence-Based Classification of Chest X-Ray Images into COVID-19 and Other Infectious Diseases
- PMID: 33061946
- PMCID: PMC7539085
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8889023
Artificial Intelligence-Based Classification of Chest X-Ray Images into COVID-19 and Other Infectious Diseases
Abstract
The ongoing pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has led to global health and healthcare crisis, apart from the tremendous socioeconomic effects. One of the significant challenges in this crisis is to identify and monitor the COVID-19 patients quickly and efficiently to facilitate timely decisions for their treatment, monitoring, and management. Research efforts are on to develop less time-consuming methods to replace or to supplement RT-PCR-based methods. The present study is aimed at creating efficient deep learning models, trained with chest X-ray images, for rapid screening of COVID-19 patients. We used publicly available PA chest X-ray images of adult COVID-19 patients for the development of Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based classification models for COVID-19 and other major infectious diseases. To increase the dataset size and develop generalized models, we performed 25 different types of augmentations on the original images. Furthermore, we utilized the transfer learning approach for the training and testing of the classification models. The combination of two best-performing models (each trained on 286 images, rotated through 120° or 140° angle) displayed the highest prediction accuracy for normal, COVID-19, non-COVID-19, pneumonia, and tuberculosis images. AI-based classification models trained through the transfer learning approach can efficiently classify the chest X-ray images representing studied diseases. Our method is more efficient than previously published methods. It is one step ahead towards the implementation of AI-based methods for classification problems in biomedical imaging related to COVID-19.
Copyright © 2020 Arun Sharma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
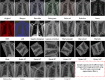
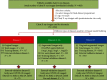
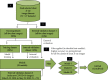
References
-
- WHO. Naming the coronavirus disease (covid-19) and the virus that causes it. WHO; 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technica....
-
- Hui D. S., I Azhar E., Madani T. A., et al. The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health - the latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. International journal of infectious diseases. 2020;91:264–266. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO. Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19-11 March 2020. WHO; 2020. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re....
-
- WHO. Pneumonia of unknown cause-China. WHO; 2020. https://www.who.int/csr/don/05-january-2020-pneumonia-of-unkown-cause-ch...
-
- WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. 2020. September 2020, https://covid19.who.int/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

