Metabolic Effects of Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus or Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33061966
- PMCID: PMC7545471
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4732021
Metabolic Effects of Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus or Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is commonly used for the treatment of hypogonadism in men, which is often associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and metabolic syndrome (Mets). Recent compiling evidence shows that TRT has beneficial metabolic effects on these patients.
Objective: A meta-analysis has been conducted to evaluate the effects of TRT on cardiovascular metabolic factors.
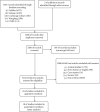
Methods: We conducted a systemic search on PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Wanfang, and CNKI and selected randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to include. The efficacy of TRT on glycemia, insulin sensitivity, lipid profile, and body weight was meta-analyzed by Review Manager.
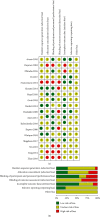
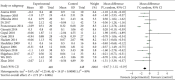
Results: A total of 18 RCTs, containing 1415 patients (767 in TRT and 648 in control), were enrolled for the meta-analysis. The results showed that TRT could reduce HbA1c (MD = -0.67, 95% CI -1.35, -0.19, and P=0.006) and improve HOMA-IR (homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance) (SMD = -1.94, 95% CI -2.65, -1.23, and P < 0.0001). TRT could also decrease low-density lipoprotein (SMD = -0.50, 95% CI -0.82, -0.90, and P=0.002) and triglycerides (MD = -0.64, 95% CI -0.91, -0.36, and P < 0.0001). In addition, TRT could reduce body weight by 3.91 kg (MD = -3.91, 95% CI -4.14, -3.69, and P < 0.00001) and waist circumference by 2.8 cm (MD -2.80, 95% CI -4.38, -1.21 and P=0.0005). Erectile dysfunction (measured by IIEF-5) did not improve, while aging-related symptoms (measured by AMS scores) significantly improved.
Conclusions: TRT improves glycemic control, insulin sensitivity, and lipid parameters in hypogonadism patients with T2DM and MetS, partially through reducing central obesity.
Copyright © 2020 Shu-ying Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

