Circadian Profile of Salivary Melatonin Secretion in Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy
- PMID: 33061967
- PMCID: PMC7533010
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6209841
Circadian Profile of Salivary Melatonin Secretion in Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy
Abstract
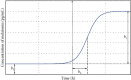
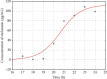
Purpose: In the present study, the salivary melatonin secretion in the hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) children was measured. The logit model was fitted to the data to obtain the salivary dim light melatonin onsets (DLMOs), and the results were compared with the values estimated from the classic threshold method with a linear interpolation and those previously published for the blood measurements.
Materials and methods: 9 patients suffering from HIE aged from 65 to 80 months were included in the study. The melatonin levels were assessed by a radioimmunoassay (RIA). The diurnal melatonin secretion was estimated using a nonlinear least squares method. Student's t-test and the Mann-Whitney U test were used for the comparisons of the obtained parameters.
Results: The circadian profiles of the melatonin secretion for both calculation methods do not differ statistically. The DLMO parameters obtained in the blood and saliva samples in children with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy were similar.
Copyright © 2020 Łukasz Kapek et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An independent comparison of the Novolytix salivary melatonin radioimmunoassay with the new Novolytix salivary melatonin enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.J Pineal Res. 2024 Jan;76(1):e12933. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12933. Epub 2023 Dec 18. J Pineal Res. 2024. PMID: 38108222 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating the dim light melatonin onset of adolescents within a 6-h sampling window: the impact of sampling rate and threshold method.Sleep Med. 2016 Apr;20:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2015.11.019. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Sleep Med. 2016. PMID: 27318227 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of dim light melatonin onset based on plasma and saliva samples.Chronobiol Int. 2022 May;39(5):626-635. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2021.2016796. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Chronobiol Int. 2022. PMID: 35168448
-
Why the dim light melatonin onset (DLMO) should be measured before treatment of patients with circadian rhythm sleep disorders.Sleep Med Rev. 2014 Aug;18(4):333-9. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Sleep Med Rev. 2014. PMID: 24388969 Review.
-
Dim light melatonin onset (DLMO): a tool for the analysis of circadian phase in human sleep and chronobiological disorders.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Jan 30;31(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2006.06.020. Epub 2006 Aug 1. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 16884842 Review.
References
-
- Paprocka J., Kijonka M., Sokół M. Drăgoi C. M., Nicolae A. C. Melatonin in Childhood Epilepsy and in Child Neurology”, Melatonin-Molecular Biology, Clinical and Pharmaceutical Approaches. London, UK: IntechOpen; 2018. - DOI
-
- Paprocka J., Kijonka M., Borys D., Emich-Widera E, Wojcieszek P, Sokół M. Mathematical evaluation of melatonin secretion in hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Neuro Endocrinology Letters. 2018;39(5):391–400. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

