Dipteran Carboxymethyl Chitosan as an Inexhaustible Derivative with a Potential Antiproliferative Activity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 33062011
- PMCID: PMC7539079
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4396305
Dipteran Carboxymethyl Chitosan as an Inexhaustible Derivative with a Potential Antiproliferative Activity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
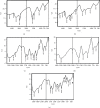
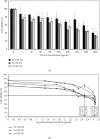
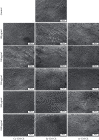
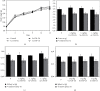
Traditional folk therapies indicate that insects have diverse medicinal potentials. However, the therapeutic application of insect chitosan and its derivatives has not been explored. To investigate the application of chitosan and its derivatives, the carboxymethyl derivative of chitosan (CM-Ch) was extracted from two dipteran larvae species, Chrysomya albiceps and Sarcophaga aegyptiaca. The degree of deacetylation (DD) and CM-Ch functional groups were validated using Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy analysis and proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H NMR), respectively. The molecular weight was estimated using MALDI-TOF MS analysis. The effect of CM-Ch on the morphology and proliferation of human liver HepG2 cancer cells was assessed. IC50 of CM-Ch induced significant growth-inhibitory effects in HepG2 cells. CM-Ch treatment altered the morphology of HepG2 in a dose-dependent manner and induced apoptosis in a caspase-dependent manner. CM-Ch treatment showed no signs of toxicity, and no alterations in liver and kidney biochemical markers were observed in albino rats. A CM-Ch derivative from commercial crustacean chitosan was used to assess the efficacy of the insect-derived CM-Ch. The data presented here introduce insect CM-Ch as a promising, inexhaustible, safe derivative of chitosan with antitumor potential in liver cancer. This is the first report highlighting the anticancer activity of insect CM-Ch in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Copyright © 2020 Rana M. Abdel Rahman et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of chitosan from the blowfly Chrysomya megacephala larvae.Int J Biol Macromol. 2013 Sep;60:347-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.05.039. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013. PMID: 23792633
-
New thiadiazole modified chitosan derivative to control the growth of human pathogenic microbes and cancer cell lines.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 11;12(1):21423. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25772-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36503959 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of carboxymethyl chitosan synthesis using response surface methodology and desirability function.Int J Biol Macromol. 2016 Apr;85:615-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.01.017. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016. PMID: 26778157
-
Selective anticancer activity of hydroxyapatite/chitosan-poly(d,l)-lactide-co-glycolide particles loaded with an androstane-based cancer inhibitor.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016 Dec 1;148:629-639. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.09.041. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016. PMID: 27694053 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of synthetic PDE-5 inhibitors and their analogues as adulterants: analytical techniques and challenges.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;87:176-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.04.037. Epub 2013 May 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 23721687 Review.
Cited by
-
Unravelling the potential of insects for medicinal purposes - A comprehensive review.Heliyon. 2023 Apr 29;9(5):e15938. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15938. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37206028 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- El-Sherif A. A. S. Diagnostic outcomes of soluble major histocompatibility complex class I related chain molecule A and des-[gamma] carboxy prothrombin versus alpha-FetoProtein for hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients. Immunome Research. 2016;12(3):p. 1.
-
- Ai H., Wang F., Yang Q., Zhu F., Lei C. Preparation and biological activities of chitosan from the larvae of housefly, Musca domestica. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2008;72(3):419–423. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.09.010. - DOI
-
- Feng Y., Zhao M., He Z., Chen Z., Sun L. Research and utilization of medicinal insects in China. Entomological Research. 2009;39(5):313–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-5967.2009.00236.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

