Clinical and Radiological Characterization of Patients with Immobilizing and Progressive Stress Fractures in Methotrexate Osteopathy
- PMID: 33064170
- PMCID: PMC7819927
- DOI: 10.1007/s00223-020-00765-5
Clinical and Radiological Characterization of Patients with Immobilizing and Progressive Stress Fractures in Methotrexate Osteopathy
Abstract
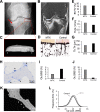
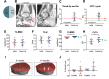
Methotrexate (MTX) is one of the most commonly prescribed drugs for autoimmune rheumatic diseases. As there is no consensus on its negative effects on bone, the purpose of this investigation was to determine the clinical spectrum of patients with stress fractures due to long-term MTX treatment (i.e., MTX osteopathy). We have retrospectively analyzed data from 34 patients with MTX treatment, severe lower extremity pain and immobilization. MRI scans, bone turnover markers, bone mineral density (DXA) and bone microarchitecture (HR-pQCT) were evaluated. Stress fractures were also imaged with cone beam CT. While the time between clinical onset and diagnosis was prolonged (17.4 ± 8.6 months), the stress fractures had a pathognomonic appearance (i.e., band-/meander-shaped, along the growth plate) and were diagnosed in the distal tibia (53%), the calcaneus (53%), around the knee (62%) and at multiple sites (68%). Skeletal deterioration was expressed by osteoporosis (62%) along with dissociation of low bone formation and increased bone resorption. MTX treatment was discontinued in 27/34 patients, and a combined denosumab-teriparatide treatment initiated. Ten patients re-evaluated at follow-up (2.6 ± 1.5 years) had improved clinically in terms of successful remobilization. Taken together, our findings provide the first in-depth skeletal characterization of patients with pathognomonic stress fractures after long-term MTX treatment.
Keywords: Cone beam CT; Denosumab; MTX osteopathy; Methotrexate; Stress fracture; Teriparatide.
Conflict of interest statement
Tim Rolvien, Nico Maximilian Jandl, Julian Stürznickel, Frank Timo Beil, Ina Kötter, Ralf Oheim, Ansgar W Lohse, Florian Barvencik and Michael Amling declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Constantin A, Loubet-Lescoulie P, Lambert N, Yassine-Diab B, Abbal M, Mazieres B, de Preval C, Cantagrel A. Antiinflammatory and immunoregulatory action of methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: evidence of increased interleukin-4 and interleukin-10 gene expression demonstrated in vitro by competitive reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41:48–57. - PubMed
-
- Wessels JA, Huizinga TW, Guchelaar HJ. Recent insights in the pharmacological actions of methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47:249–255. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz AM, Leonidas JC. Methotrexate osteopathy. Skelet Radiol. 1984;11:13–16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

