Impact of Human SULT1E1 Polymorphisms on the Sulfation of 17β-Estradiol, 4-Hydroxytamoxifen, and Diethylstilbestrol by SULT1E1 Allozymes
- PMID: 33064293
- PMCID: PMC7855807
- DOI: 10.1007/s13318-020-00653-1
Impact of Human SULT1E1 Polymorphisms on the Sulfation of 17β-Estradiol, 4-Hydroxytamoxifen, and Diethylstilbestrol by SULT1E1 Allozymes
Abstract
Background and objectives: Previous studies have revealed that sulfation, as mediated by the estrogen-sulfating cytosolic sulfotransferase (SULT) SULT1E1, is involved in the metabolism of 17β-estradiol (E2), 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4OH-tamoxifen), and diethylstilbestrol in humans. It is an interesting question whether the genetic polymorphisms of SULT1E1, the gene that encodes the SULT1E1 enzyme, may impact on the metabolism of E2 and these two drug compounds through sulfation.
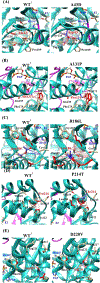
Methods: In this study, five missense coding single nucleotide polymorphisms of the SULT1E1 gene were selected to investigate the sulfating activity of the coded SULT1E1 allozymes toward E2, 4OH-tamoxifen, and diethylstilbestrol. Corresponding cDNAs were generated by site-directed mutagenesis, and recombinant SULT1E1 allozymes were bacterially expressed, affinity-purified, and characterized using enzymatic assays.
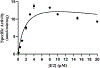
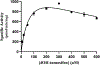
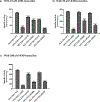
Results: Purified SULT1E1 allozymes were shown to display differential sulfating activities toward E2, 4OH-tamoxifen, and diethylstilbestrol. Kinetic analysis revealed further distinct Km (reflecting substrate affinity) and Vmax (reflecting catalytic activity) values of the five SULT1E1 allozymes with E2, 4OH-tamoxifen, and diethylstilbestrol as substrates.
Conclusions: Taken together, these findings highlighted the significant differences in E2-, as well as the drug-sulfating activities of SULT1E1 allozymes, which may have implications in the differential metabolism of E2, 4OH-tamoxifen, and diethylstilbestrol in individuals with different SULT1E1 genotypes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Crewe HK, Notley LM, Wunsch RM, Lennard MS, Gillam EM. Metabolism of tamoxifen by recombinant human cytochrome P450 enzymes: formation of the 4-hydroxy, 4’-hydroxy and N-desmethyl metabolites and isomerization of trans-4-hydroxytamoxifen. Drug Metab Dispos 2002;30(8):869–74. 10.1124/dmd.30.8.869 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

