Structures of a Complete Human V-ATPase Reveal Mechanisms of Its Assembly
- PMID: 33065002
- PMCID: PMC7655608
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.09.029
Structures of a Complete Human V-ATPase Reveal Mechanisms of Its Assembly
Abstract
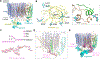
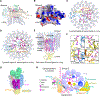
Vesicular- or vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases) are ATP-driven proton pumps comprised of a cytoplasmic V1 complex for ATP hydrolysis and a membrane-embedded Vo complex for proton transfer. They play important roles in acidification of intracellular vesicles, organelles, and the extracellular milieu in eukaryotes. Here, we report cryoelectron microscopy structures of human V-ATPase in three rotational states at up to 2.9-Å resolution. Aided by mass spectrometry, we build all known protein subunits with associated N-linked glycans and identify glycolipids and phospholipids in the Vo complex. We define ATP6AP1 as a structural hub for Vo complex assembly because it connects to multiple Vo subunits and phospholipids in the c-ring. The glycolipids and the glycosylated Vo subunits form a luminal glycan coat critical for V-ATPase folding, localization, and stability. This study identifies mechanisms of V-ATPase assembly and biogenesis that rely on the integrated roles of ATP6AP1, glycans, and lipids.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests H.W. is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Cell. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
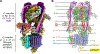



Comment in
-
A "Sugar-Coated" Proton Pump Comes into Focus: High-Resolution Structure of a Human V-ATPase.Mol Cell. 2020 Nov 5;80(3):379-380. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.020. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 33157012
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

