Vascular Disease and Thrombosis in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Rhesus Macaques
- PMID: 33065030
- PMCID: PMC7546181
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.005
Vascular Disease and Thrombosis in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Rhesus Macaques
Abstract
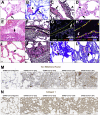
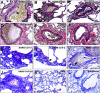
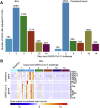
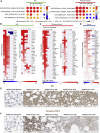
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to extensive morbidity and mortality throughout the world. Clinical features that drive SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis in humans include inflammation and thrombosis, but the mechanistic details underlying these processes remain to be determined. In this study, we demonstrate endothelial disruption and vascular thrombosis in histopathologic sections of lungs from both humans and rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2. To define key molecular pathways associated with SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis in macaques, we performed transcriptomic analyses of bronchoalveolar lavage and peripheral blood and proteomic analyses of serum. We observed macrophage infiltrates in lung and upregulation of macrophage, complement, platelet activation, thrombosis, and proinflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein, MX1, IL-6, IL-1, IL-8, TNFα, and NF-κB. These results suggest a model in which critical interactions between inflammatory and thrombosis pathways lead to SARS-CoV-2-induced vascular disease. Our findings suggest potential therapeutic targets for COVID-19.
Keywords: IFNα; SARS-CoV-2; coagulation; collagen; complement; macrophage; platelet; thrombosis; vWF; vascular.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



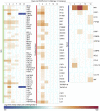
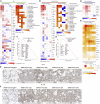
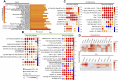
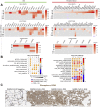



References
-
- Bikdeli B., Madhavan M.V., Jimenez D., Chuich T., Dreyfus I., Driggin E., Nigoghossian C., Ageno W., Madjid M., Guo Y., et al. Global COVID-19 Thrombosis Collaborative Group, Endorsed by the ISTH, NATF, ESVM, and the IUA, Supported by the ESC Working Group on Pulmonary Circulation and Right Ventricular Function COVID-19 and Thrombotic or Thromboembolic Disease: Implications for Prevention, Antithrombotic Therapy, and Follow-Up: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:2950–2973. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P51 OD011092/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA260476/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025002/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026799/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AI118672/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI124377/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI128751/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI129797/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007387/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA225088/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI149670/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI126603/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI135098/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 OD024917/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

