The role of kallikrein-kinin and renin-angiotensin systems in COVID-19 infection
- PMID: 33065209
- PMCID: PMC7553876
- DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2020.170428
The role of kallikrein-kinin and renin-angiotensin systems in COVID-19 infection
Abstract
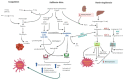
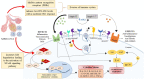
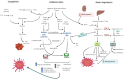
In November 2019 the first cases of a novel acute respiratory syndrome has been reported in Wuhan province, China. Soon after, in January 2020 the World Health Organization declared a pandemic state due to the dissemination of a virus named SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2), the cause of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Being an unknown disease, it is essential to assess not only its main characteristic features and overall clinical symptomatology but also its patient infection mode and propagation to design appropriate clinical interventions and treatments. In this review the pathophysiology of SARS-CoV-2 infection and how the virus enters the cells and activates the immune system are described. The role of three systems involved in the SARS- CoV-2 infection (renin-angiotensin, kinin and coagulation systems) is discussed with the objectives to identify and try to explain several of the events observed during the evolution of the disease and to suggest possible targets for therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coagulation system; Kallikrein-kinin system; Kinins; Renin-angiotensin system.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Zhenming J., Yao Z., Yuan S., Bing Z., Haofeng Z., Yan W., Yan Z., Chen Z., Tianyu T., Xiaoyu D., Yinkai D., Jing Y., Xiaobao Y., Xiuna Y., Kailin Y., Xiang L., Luke G., Gengfu X., Leike Z., Haitao Y., Zihe R. Structural basis for the inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 main protease by antineoplastic drug carmofur. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020;27:529–532. - PubMed
-
- Huang M.M.X., Fengxiang W., Liang H., Lijuan W.M.M., Chen M.M.K. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of COVID-19. Arch. Iran. Med. 2020;23:268–271. - PubMed
-
- Bourgonje A.R., Abdulle A.E., Timens W., Hillebrands J.L., Navis G.J., Gordijn S.J., Bolling C., Dijkstra G., Voors A.A., Osterhaus A.D.M.S., van der Voort P.H.J., Mulder D.J., van Goor H. Angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) J. Pathol. 2020;251:228–248. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

