Sexual dimorphism in the nociceptive effects of hyaluronan
- PMID: 33065736
- PMCID: PMC7969372
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002116
Sexual dimorphism in the nociceptive effects of hyaluronan
Abstract
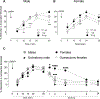
Intradermal administration of low-molecular-weight hyaluronan (LMWH) in the hind paw induced dose-dependent (0.1, 1, or 10 µg) mechanical hyperalgesia of similar magnitude in male and female rats. However, the duration of LMWH hyperalgesia was greater in females. This sexual dimorphism was eliminated by bilateral ovariectomy and by intrathecal administration of an oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) antisense to the G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPR30) mRNA in females, indicating estrogen dependence. To assess the receptors at which LMWH acts to induce hyperalgesia, LMWH was administered to groups of male and female rats that had been pretreated with ODN antisense (or mismatch) to the mRNA for 1 of 3 hyaluronan receptors, cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44), toll-like receptor 4, or receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility (RHAMM). Although LMWH-induced hyperalgesia was attenuated in both male and female rats pretreated with ODN antisense for CD44 and toll-like receptor 4 mRNA, RHAMM antisense pretreatment only attenuated LMWH-induced hyperalgesia in males. Oligodeoxynucleotide antisense for RHAMM, however, attenuated LMWH-induced hyperalgesia in female rats treated with ODN antisense to GPR30, as well as in ovariectomized females. Low-molecular-weight hyaluronan-induced hyperalgesia was significantly attenuated by pretreatment with high-molecular-weight hyaluronan (HMWH) in male, but not in female rats. After gonadectomy or treatment with ODN antisense to GPR30 expression in females, HMWH produced similar attenuation of LMWH-induced hyperalgesia to that seen in males. These experiments identify nociceptors at which LMWH acts to produce mechanical hyperalgesia, establishes estrogen dependence in the role of RHAMM in female rats, and establishes estrogen dependence in the inhibition of LMWH-induced hyperalgesia by HMWH.
Copyright © 2020 International Association for the Study of Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


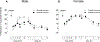
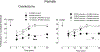
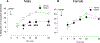

References
-
- Ageberg E, Forssblad M, Herbertsson P, Roos EM. Sex differences in patient-reported outcomes after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: data from the Swedish knee ligament register. Am J Sports Med 2010; 38: 1334–1342. - PubMed
-
- Al’Qteishat A, Gaffney J, Krupinski J, Rubio F, West D, Kumar S, Kumar P, Mitsios N, Slevin M. Changes in hyaluronan production and metabolism following ischaemic stroke in man. Brain 2006; 129: 2158–2176. - PubMed
-
- Alessandri-Haber N, Yeh JJ, Boyd AE, Parada CA, Chen X, Reichling DB, Levine JD. Hypotonicity induces TRPV4-mediated nociception in rat. Neuron 2003; 39: 497–511. - PubMed

