Characterization of Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Peptides from Soft-Shelled Turtle Yolk Hydrolysate Using Orthogonal Bioassay-Guided Fractionations Coupled with In Vitro and In Silico Study
- PMID: 33066488
- PMCID: PMC7602288
- DOI: 10.3390/ph13100308
Characterization of Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Peptides from Soft-Shelled Turtle Yolk Hydrolysate Using Orthogonal Bioassay-Guided Fractionations Coupled with In Vitro and In Silico Study
Abstract
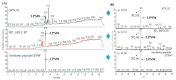
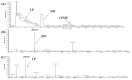
Five novel peptides (LPLF, WLQL, LPSW, VPGLAL, and LVGLPL) bearing dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory activities were identified from the gastrointestinal enzymatic hydrolysate of soft-shelled turtle yolk (SSTY) proteins. Peptides were isolated separately using reversed-phase (RP) chromatography in parallel with off-line strong cation exchange (SCX) chromatography followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis to determine sequences. Among these peptides, LPSW showed the highest DPP-IV inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 269.7 ± 15.91 µM. The results of the pre-incubation experiment and the kinetic study of these peptides indicated that WLQL is a true inhibitor and its inhibition toward DPP-IV is of an uncompetitive model, while LPLF, LPSW, and VPGLAL are real-substrates and competitive inhibitors against DPP-IV. The DPP-IV inhibitory peptides derived from SSTY hydrolysate in study are promising in the management of hyperglycemia in Type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: DPP-IV inhibitory peptides; LC-MS/MS; bioassay-guided fractionation; in silico analysis; soft-shelled turtle yolk protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures













References
-
- Chiu L.H., Hsu G.S.W., Lu Y.F. Antihypertensive capacity of defatted soft-shelled turtle powder after hydrolysis by gastrointestinal enzymes. J. Food Biochem. 2006;30:589–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4514.2006.00087.x. - DOI
-
- Yu H., Li Y., Wang J., Zheng L., Yan W. Chinese soft-shelled turtle egg powder lowers serum cholesterol, increases faecal neutral steroids and bile acid excretion, and up-regulates liver cytochrome P450 mRNA level in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2005;94:315–320. - PubMed
-
- Liu L., Lu B., Gong L., Wu X., Zhang Y. Studies on bioactive peptide from Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) with functionalities of ACE inhibition and antioxidation. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012;11:6723–6729.
-
- Pujiastuti D.Y., Shih Y.H., Chen W.L., Hsu J.L. Screening of angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from soft-shelled turtle yolk using two orthogonal bioassay-guided fractionations. J. Funct. Foods. 2017;28:36–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2016.10.029. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

