β-Secretase1 biological markers for Alzheimer's disease: state-of-art of validation and qualification
- PMID: 33066807
- PMCID: PMC7566058
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-020-00686-3
β-Secretase1 biological markers for Alzheimer's disease: state-of-art of validation and qualification
Abstract
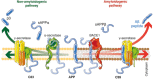
β-Secretase1 (BACE1) protein concentrations and rates of enzyme activity, analyzed in human bodily fluids, are promising candidate biological markers for guidance in clinical trials investigating BACE1 inhibitors to halt or delay the dysregulation of the amyloid-β pathway in Alzheimer's disease (AD). A robust body of evidence demonstrates an association between cerebrospinal fluid/blood BACE1 biomarkers and core pathophysiological mechanisms of AD, such as brain protein misfolding and aggregration, neurodegeneration, and synaptic dysfunction.In pharmacological trials, BACE1 candidate biomarkers may be applied to a wide set of contexts of use (CoU), including proof of mechanism, dose-finding, response and toxicity dose estimation. For clinical CoU, BACE1 biomarkers show good performance for prognosis and disease prediction.The roadmap toward validation and qualification of BACE1 biomarkers requires standardized pre-analytical and analytical protocols to reduce inter-site variance that may have contributed to inconsistent results.BACE1 biomarker-drug co-development programs, including biomarker-guided outcomes and endpoints, may support the identification of sub-populations with a higher probability to benefit from BACE1 inhibitors with a reduced risk of adverse effects, in line with the evolving precision medicine paradigm.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid-β pathway; Axonal damage; BACE1; Clinical trials; Context of use; Fluid biomarkers; Neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
HH is an employee of Eisai Inc. This work has been performed during his previous position at Sorbonne University, Paris, France. At Sorbonne University, he was supported by the AXA Research Fund, the “Fondation partenariale Sorbonne Université,” and the “Fondation pour la Recherche sur Alzheimer,” Paris, France. HH serves as Senior Associate Editor for the journal
He is a co-inventor in the following patents as a scientific expert and has received no royalties:
• In Vitro Multiparameter Determination Method for The Diagnosis and Early Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Disorders Patent Number: 8916388.
• In Vitro Procedure for Diagnosis and Early Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Diseases Patent Number: 8298784.
• Neurodegenerative Markers for Psychiatric Conditions Publication Number: 20120196300.
• In Vitro Multiparameter Determination Method for The Diagnosis and Early Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Disorders Publication Number: 20100062463.
• In Vitro Method for The Diagnosis and Early Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Disorders Publication Number: 20100035286.
• In Vitro Procedure for Diagnosis and Early Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Diseases Publication Number: 20090263822.
• In Vitro Method for The Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Diseases Patent Number: 7547553.
• CSF Diagnostic in Vitro Method for Diagnosis of Dementias and Neuroinflammatory Diseases Publication Number: 20080206797.
• In Vitro Method for The Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Diseases Publication Number: 20080199966.
• Neurodegenerative Markers for Psychiatric Conditions Publication Number: 20080131921.
SL received lecture honoraria from Roche and Servier.
AV is an employee of Eisai Inc. This work has been performed during his previous position at Sorbonne University, Paris, France. He does not receive any fees or honoraria since November 2019. Before November 2019, he had received lecture honoraria from Roche, MagQu LLC, and Servier.
HZ has served at scientific advisory boards for Roche Diagnostics, Denali, Wave, Samumed, and CogRx; has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Alzecure and Biogen; and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB, a GU Ventures-based platform company at the University of Gothenburg.
KB has served as a consultant or at advisory boards for Abcam, Axon, Biogen, Lilly, MagQu, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB, a GU Venture-based platform company at the University of Gothenburg, all unrelated to the work presented in this paper.
ADV, FSG, AG, FC, BD, and YR report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kandalepas PC, Sadleir KR, Eimer WA, Zhao J, Nicholson DA, Vassar R. The Alzheimer’s beta-secretase BACE1 localizes to normal presynaptic terminals and to dystrophic presynaptic terminals surrounding amyloid plaques. Acta Neuropathol. 2013;126:329–352. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1152-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

