Metformin enhances anti-mycobacterial responses by educating CD8+ T-cell immunometabolic circuits
- PMID: 33067434
- PMCID: PMC7567856
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19095-z
Metformin enhances anti-mycobacterial responses by educating CD8+ T-cell immunometabolic circuits
Abstract
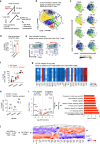
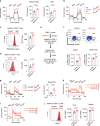
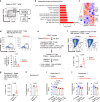
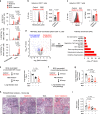
Patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) have a lower risk of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, progression from infection to tuberculosis (TB) disease, TB morality and TB recurrence, when being treated with metformin. However, a detailed mechanistic understanding of these protective effects is lacking. Here, we use mass cytometry to show that metformin treatment expands a population of memory-like antigen-inexperienced CD8+CXCR3+ T cells in naive mice, and in healthy individuals and patients with T2D. Metformin-educated CD8+ T cells have increased (i) mitochondrial mass, oxidative phosphorylation, and fatty acid oxidation; (ii) survival capacity; and (iii) anti-mycobacterial properties. CD8+ T cells from Cxcr3-/- mice do not exhibit this metformin-mediated metabolic programming. In BCG-vaccinated mice and guinea pigs, metformin enhances immunogenicity and protective efficacy against M. tuberculosis challenge. Collectively, these results demonstrate an important function of CD8+ T cells in metformin-derived host metabolic-fitness towards M. tuberculosis infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

