Whole-genome sequencing of acral melanoma reveals genomic complexity and diversity
- PMID: 33067454
- PMCID: PMC7567804
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18988-3
Whole-genome sequencing of acral melanoma reveals genomic complexity and diversity
Abstract
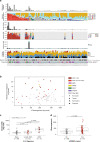
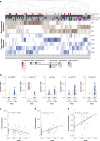
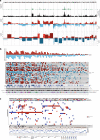
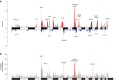
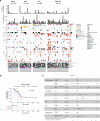
To increase understanding of the genomic landscape of acral melanoma, a rare form of melanoma occurring on palms, soles or nail beds, whole genome sequencing of 87 tumors with matching transcriptome sequencing for 63 tumors was performed. Here we report that mutational signature analysis reveals a subset of tumors, mostly subungual, with an ultraviolet radiation signature. Significantly mutated genes are BRAF, NRAS, NF1, NOTCH2, PTEN and TYRP1. Mutations and amplification of KIT are also common. Structural rearrangement and copy number signatures show that whole genome duplication, aneuploidy and complex rearrangements are common. Complex rearrangements occur recurrently and are associated with amplification of TERT, CDK4, MDM2, CCND1, PAK1 and GAB2, indicating potential therapeutic options.
Conflict of interest statement
J.V.P. and N.W. are founders and shareholders of genomiQa Pty Ltd, and members of its Board. R.A.S. has received fees for professional services from Merck Sharp & Dohme, GlaxoSmithKline Australia, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermpedia, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Australia Pty Ltd, Myriad, NeraCare and Amgen. G.V.L is consultant advisor for Aduro, Amgen, Array, BMS, MERCK MSD, Novartis, Pierre-Fabre, Roche, Sandoz. R.P.M.S has participated in advisory boards for MSD, Novartis and received speaking honoraria from BMS. J.F.T. has received honoraria for advisory board participation from Merck Sharpe Dohme Australia and Bristol Myers Squibb Australia. J.F.T. has also received honoraria and travel expenses from GSK and Provectus Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

