Chromosome reciprocal translocations have accompanied subspecies evolution in bananas
- PMID: 33067829
- PMCID: PMC7839431
- DOI: 10.1111/tpj.15031
Chromosome reciprocal translocations have accompanied subspecies evolution in bananas
Abstract
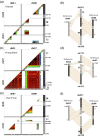
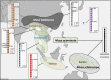
Chromosome rearrangements and the way that they impact genetic differentiation and speciation have long raised questions from evolutionary biologists. They are also a major concern for breeders because of their bearing on chromosome recombination. Banana is a major crop that derives from inter(sub)specific hybridizations between various once geographically isolated Musa species and subspecies. We sequenced 155 accessions, including banana cultivars and representatives of Musa diversity, and genotyped-by-sequencing 1059 individuals from 11 progenies. We precisely characterized six large reciprocal translocations and showed that they emerged in different (sub)species of Musa acuminata, the main contributor to currently cultivated bananas. Most diploid and triploid cultivars analyzed were structurally heterozygous for 1 to 4 M. acuminata translocations, highlighting their complex origin. We showed that all translocations induced a recombination reduction of variable intensity and extent depending on the translocations, involving only the breakpoint regions, a chromosome arm, or an entire chromosome. The translocated chromosomes were found preferentially transmitted in many cases. We explore and discuss the possible mechanisms involved in this preferential transmission and its impact on translocation colonization.
Keywords: Musa; chromosome segregation; genome evolution; reciprocal translocation; recombination.
© 2020 The Authors. The Plant Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Belser, C. , Istace, B. , Denis, E. et al (2018) Chromosome‐scale assemblies of plant genomes using nanopore long reads and optical maps. Nat. Plants, 4, 879. - PubMed
-
- Birchler, J.A. (2013) Aneuploidy in plants and flies: the origin of studies of genomic imbalance. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 24, 315–319. - PubMed
-
- Britton‐Davidian, J. , Catalan, J. , da Ramalhinho, M. , Ganem, G. , Auffray, J.‐C. , Capela, R. , Biscoito, M. , Searle, J.B. and da Luz Mathias, M. (2000) Rapid chromosomal evolution in island mice. Nature, 403, 158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

