Aß40 displays amyloidogenic properties in the non-transgenic mouse brain but does not exacerbate Aß42 toxicity in Drosophila
- PMID: 33069251
- PMCID: PMC7568834
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-020-00698-z
Aß40 displays amyloidogenic properties in the non-transgenic mouse brain but does not exacerbate Aß42 toxicity in Drosophila
Abstract
Background: Self-assembly of the amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide into aggregates, from small oligomers to amyloid fibrils, is fundamentally linked with Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, it is clear that not all forms of Aβ are equally harmful and that linking a specific aggregate to toxicity also depends on the assays and model systems used (Haass et al., J Biol. Chem 269:17741-17748, 1994; Borchelt et al., Neuron 17:1005-1013, 1996). Though a central postulate of the amyloid cascade hypothesis, there remain many gaps in our understanding regarding the links between Aβ deposition and neurodegeneration.
Methods: In this study, we examined familial mutations of Aβ that increase aggregation and oligomerization, E22G and ΔE22, and induce cerebral amyloid angiopathy, E22Q and D23N. We also investigated synthetic mutations that stabilize dimerization, S26C, and a phospho-mimetic, S8E, and non-phospho-mimetic, S8A. To that end, we utilized BRI2-Aβ fusion technology and rAAV2/1-based somatic brain transgenesis in mice to selectively express individual mutant Aβ species in vivo. In parallel, we generated PhiC31-based transgenic Drosophila melanogaster expressing wild-type (WT) and Aβ40 and Aβ42 mutants, fused to the Argos signal peptide to assess the extent of Aβ42-induced toxicity as well as to interrogate the combined effect of different Aβ40 and Aβ42 species.
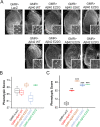
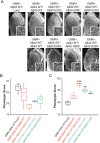
Results: When expressed in the mouse brain for 6 months, Aβ42 E22G, Aβ42 E22Q/D23N, and Aβ42WT formed amyloid aggregates consisting of some diffuse material as well as cored plaques, whereas other mutants formed predominantly diffuse amyloid deposits. Moreover, while Aβ40WT showed no distinctive phenotype, Aβ40 E22G and E22Q/D23N formed unique aggregates that accumulated in mouse brains. This is the first evidence that mutant Aβ40 overexpression leads to deposition under certain conditions. Interestingly, we found that mutant Aβ42 E22G, E22Q, and S26C, but not Aβ40, were toxic to the eye of Drosophila. In contrast, flies expressing a copy of Aβ40 (WT or mutants), in addition to Aβ42WT, showed improved phenotypes, suggesting possible protective qualities for Aβ40.
Conclusions: These studies suggest that while some Aβ40 mutants form unique amyloid aggregates in mouse brains, they do not exacerbate Aβ42 toxicity in Drosophila, which highlights the significance of using different systems for a better understanding of AD pathogenicity and more accurate screening for new potential therapies.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid plaques; Cognitive impairment; Drosophila; Fruit fly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neurotoxicity and physicochemical properties of Abeta mutant peptides from cerebral amyloid angiopathy: implication for the pathogenesis of cerebral amyloid angiopathy and Alzheimer's disease.J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 14;278(46):46179-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301874200. Epub 2003 Aug 27. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12944403
-
Anti-Parallel β-Hairpin Structure in Soluble Aβ Oligomers of Aβ40-Dutch and Aβ40-Iowa.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 27;22(3):1225. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031225. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33513738 Free PMC article.
-
Short Aβ peptides attenuate Aβ42 toxicity in vivo.J Exp Med. 2018 Jan 2;215(1):283-301. doi: 10.1084/jem.20170600. Epub 2017 Dec 5. J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29208777 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic effects of cerebral amyloid angiopathy mutations in the amyloid beta-protein precursor.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Nov;977:258-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04824.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. PMID: 12480759 Review.
-
Distinctive contribution of two additional residues in protein aggregation of Aβ42 and Aβ40 isoforms.BMB Rep. 2024 Jun;57(6):263-272. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2024-0044. BMB Rep. 2024. PMID: 38835114 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting PSEN1 by lnc-CYP3A43-2/miR-29b-2-5p to Reduce β Amyloid Plaque Formation and Improve Cognition Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 11;23(18):10554. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810554. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142465 Free PMC article.
-
Fecal Implants From App NL-G-F and App NL-G-F/E4 Donor Mice Sufficient to Induce Behavioral Phenotypes in Germ-Free Mice.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Feb 8;16:791128. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.791128. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35210996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang R, Sweeney D, Gandy SE, Sisodia SS. The profile of soluble amyloid beta protein in cultured cell media. Detection and quantification of amyloid beta protein and variants by immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(50):31894–31902. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.50.31894. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

