A review of the ethnobotanical value, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicity and quality control of Tussilago farfara L. (coltsfoot)
- PMID: 33069788
- PMCID: PMC7561605
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113478
A review of the ethnobotanical value, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicity and quality control of Tussilago farfara L. (coltsfoot)
Abstract
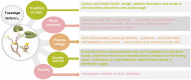
Ethnopharmacological relevance: Tussilago farfara L. (commonly called coltsfoot), known as a vital folk medicine, have long been used to treat various respiratory disorders and consumed as a vegetable in many parts of the world since ancient times.
Aim of the review: This review aims to provide a critical evaluation of the current knowledge on the ethnobotanical value, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicity and quality control of coltsfoot, thus provide a basis for further investigations.
Materials and methods: A detailed literature search was obtained using various online search engines (e.g. Google Scholar, Web of Science, Science Direct, Baidu Scholar, PubMed and CNKI). Additional information was sourced from ethnobotanical literature focusing on Chinese and European flora. The plant synonyms were validated by the database 'The Plant List' (www.theplantlist.org).
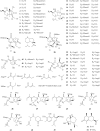
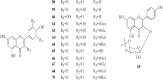
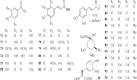
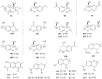
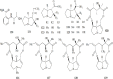
Results: Coltsfoot has diverse uses in local and traditional medicine, but similarities have been noticed, specifically for relieving inflammatory conditions, respiratory and infectious diseases in humans. Regarding its pharmacological activities, many traditional uses of coltsfoot are supported by modern in vitro or in vivo pharmacological studies such as anti-inflammatory activities, neuro-protective activity, anti-diabetic, anti-oxidant activity. Quantitative analysis (e.g. GC-MS, UHPLC-MRMHR) indicated the presence of a rich (>150) pool of chemicals, including sesquiterpenes, phenolic acids, flavonoids, chromones, pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) and others from its leaves and buds. In addition, adverse events have resulted from a collection of the wrong plant which contains PAs that became the subject of public concern attributed to their highly toxic.
Conclusions: So far, remarkable progress has been witnessed in phytochemistry and pharmacology of coltsfoot. Thus, some traditional uses have been well supported and clarified by modern pharmacological studies. Discovery of therapeutic natural products and novel structures in plants for future clinical and experimental studies are still a growing interest. Furthermore, well-designed studies in vitro particularly in vivo are required to establish links between the traditional uses and bioactivities, as well as ensure safety before clinical use. In addition, the good botanical identification of coltsfoot and content of morphologically close species is a precondition for quality supervision and control. Moreover, strict quality control measures are required in the studies investigating any aspect of the pharmacology and chemistry of coltsfoot.
Keywords: Ethnopharmacology; Pharmacology; Phytochemistry; Quality control; Toxicity; Tussilago farfara L..
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

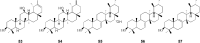
Similar articles
-
Angelica sinensis in China-A review of botanical profile, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and chemical analysis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 22;190:116-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.023. Epub 2016 May 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27211015 Review.
-
Farfarae Flos: A review of botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Oct 5;260:113038. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113038. Epub 2020 Jun 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32526340 Review.
-
Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham.: a review on its ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicity.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Aug 26;149(1):1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.05.048. Epub 2013 Jun 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23747644 Review.
-
Local and traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Sophora japonica L.: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jul 1;187:160-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.04.014. Epub 2016 Apr 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27085938 Review.
-
Genus Senecio in China: A review on its traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicity.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 May 12;347:119651. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119651. Epub 2025 Mar 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40158830 Review.
Cited by
-
An Overview of the Bioactivity of Spontaneous Medicinal Plants Suitable for the Improvement of Lung Cancer Therapies.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Mar 5;17(3):336. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17030336. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40143000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of volatile organic compounds in Farfarae flos using HS-GC-IMS across different flower colors.Food Chem X. 2025 Feb 4;26:102227. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102227. eCollection 2025 Feb. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40027114 Free PMC article.
-
How Do Herbal Cigarettes Compare To Tobacco? A Comprehensive Review of Their Sensory Characters, Phytochemicals, and Functional Properties.ACS Omega. 2022 Dec 6;7(50):45797-45809. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04708. eCollection 2022 Dec 20. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36570239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction and Characteristics of Callus Cultures of the Medicinal Plant Tussilago farfara L.Plants (Basel). 2024 Nov 1;13(21):3080. doi: 10.3390/plants13213080. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39519998 Free PMC article.
-
Allergic Potential of Medicinal Plants From the Asteraceae Family.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 23;8(2):e70398. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70398. eCollection 2025 Feb. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39995792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamczak A., Opala B., Gryszczynska A., Buchwald W. Content of pyrrolizidine alkaloids in the leaves of coltsfoot (Tussilago farfara L.) in Poland. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 2013;82(4):289–293.
-
- Boucher M.A., Cote H., Pichette A., Ripoll L., Legault J. Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of Tussilago farfara (L.) essential oil from Quebec, Canada. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018;34(4):545–548. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y., Colegate S.M., Edgar J.A. Safety assessment of food and herbal products containing hepatotoxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids: interlaboratory consistency and the importance of N-oxide determination. Phytochem. Anal. 2008;19(6):526–533. - PubMed
-
- Cao K., Xu Y., Mu X.N., Zhang Q., Wang R.J., Lv J.J. Sensitive determination of pyrrolizidine alkaloids in Tussilago farfara L. by field-amplified, sample-stacking, sweeping micellar electrokinetic chromatography. J. Separ. Sci. 2016;39(21):4243–4250. - PubMed
-
- Cheng X., Liao M., Diao X., Sun Y., Zhang L., eng Screening and identification of metabolites of two kinds of main active ingredients and hepatotoxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids in rat after lavage Farfarae Flos extract by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018;32(2) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

