Adoption of a Data-Driven Bayesian Belief Network Investigating Organizational Factors that Influence Patient Safety
- PMID: 33070320
- PMCID: PMC9291329
- DOI: 10.1111/risa.13610
Adoption of a Data-Driven Bayesian Belief Network Investigating Organizational Factors that Influence Patient Safety
Abstract
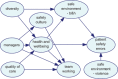
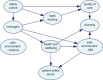
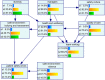
Medical errors pose high risks to patients. Several organizational factors may impact the high rate of medical errors in complex and dynamic healthcare systems. However, limited research is available regarding probabilistic interdependencies between the organizational factors and patient safety errors. To explore this, we adopt a data-driven Bayesian Belief Network (BBN) model to represent a class of probabilistic models, using the hospital-level aggregate survey data from U.K. hospitals. Leveraging the use of probabilistic dependence models and visual features in the BBN model, the results shed new light on relationships existing among eight organizational factors and patient safety errors. With the high prediction capability, the data-driven approach results suggest that "health and well-being" and "bullying and harassment in the work environment" are the two leading factors influencing the number of reported errors and near misses affecting patient safety. This study provides significant insights to understand organizational factors' role and their relative importance in supporting decision-making and safety improvements.
Keywords: Bayesian Network; healthcare operations; medical errors; patient safety; risk.
© 2020 The Authors. Risk Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Society for Risk Analysis.
Figures





References
-
- Abdelhai, R. , Abdelaziz, S. B. , & Ghanem, N. S. (2012). Assessing patient safety culture and factors affecting it among health care providers at Cairo University Hospitals. Journal of American Science, 8, 23–28.
-
- Adedipe, T. , Shafiee, M. , & Zio, E. (2020). Bayesian network modelling for the wind energy industry: An overview. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 202, 107053. 10.1016/j.ress.2020.107053 - DOI
-
- Al‐Ahmadi, T. A. (2009). Measuring patient safety culture in riyadh's hospitals: A comparison between public and private hospitals. Journal of the Egyptian Public Health Association, 84, 479–500. - PubMed
-
- Ale, B. , van Gulijk, C. , Hanea, A. , Hanea, D. , Hudson, P. , Lin, P. H. , & Sillem, S. (2014). Towards BBN based risk modelling of process plants. Safety Science, PSAM11 – ESREL 2012 69, 48–56. 10.1016/j.ssci.2013.12.007 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

