The Potential Roles of Ghrelin in Metabolic Syndrome and Secondary Symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 33071750
- PMCID: PMC7543232
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.583097
The Potential Roles of Ghrelin in Metabolic Syndrome and Secondary Symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
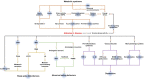
Although the major causative factors of Alzheimer's disease (AD) are the accumulation of amyloid β and hyperphosphorylated tau, AD can also be caused by metabolic dysfunction. The major clinical symptom of AD is cognitive dysfunction. However, AD is also accompanied by various secondary symptoms such as depression, sleep-wake disturbances, and abnormal eating behaviors. Interestingly, the orexigenic hormone ghrelin has been suggested to have beneficial effects on AD-related metabolic syndrome and secondary symptoms. Ghrelin improves lipid distribution and alters insulin sensitivity, effects that are hypothesized to delay the progression of AD. Furthermore, ghrelin can relieve depression by enhancing the secretion of hormones such as serotonin, noradrenaline, and orexin. Moreover, ghrelin can upregulate the expression of neurotrophic factors such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor and modulate the release of proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin 1β. Ghrelin alleviates sleep-wake disturbances by increasing the levels of melatonin, melanin-concentrating hormone. Ghrelin reduces the risk of abnormal eating behaviors by increasing neuropeptide Y and γ-aminobutyric acid. In addition, ghrelin increases food intake by inhibiting fatty acid biosynthesis. However, despite the numerous studies on the role of ghrelin in the AD-related pathology and metabolic disorders, there are only a few studies that investigate the effects of ghrelin on secondary symptoms associated with AD. In this mini review, our purpose is to provide the insights of future study by organizing the previous studies for the role of ghrelin in AD-related pathology and metabolic disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; abnormal eating behaviors; depression; ghrelin; metabolic syndrome; sleep–wake disturbances.
Copyright © 2020 Kim, Nam, Shin, Park, Jeon, Kim, Kim and Moon.
Figures
References
-
- Barazzoni R., Bosutti A., Stebel M., Cattin M. R., Roder E., Visintin L., et al. (2005). Ghrelin regulates mitochondrial-lipid metabolism gene expression and tissue fat distribution in liver and skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 288 E228–E235. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

