Lian Hua Qing Wen Capsules, a Potent Epithelial Protector in Acute Lung Injury Model, Block Proapoptotic Communication Between Macrophages, and Alveolar Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 33071777
- PMCID: PMC7538620
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.522729
Lian Hua Qing Wen Capsules, a Potent Epithelial Protector in Acute Lung Injury Model, Block Proapoptotic Communication Between Macrophages, and Alveolar Epithelial Cells
Abstract
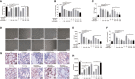
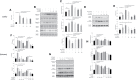
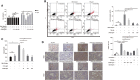
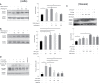
Besides pathogen evading, Acute Lung Injury (ALI), featuring the systematic inflammation and severe epithelial damages, is widely believed to be the central non-infectious factor controlling the progression of infectious diseases. ALI is partly caused by host immune responses. Under the inspiration of unsuccessful treatment in COVID-19, recent insights into pathogen-host interactions are leading to identification and development of a wide range of host-directed therapies with different mechanisms of action. The interaction unit consisting of macrophages and the alveolar epithelial cells has recently revealed as the therapeutic basis targeting ALI. Lian Hua Qing Wen capsule is the most effective and commonly-used clinical formula in treating respiratory infection for thousands of years in China. However, little is known about its relevance with ALI, especially its protective role against ALI-induced alveolar tissue damages. Aiming to evaluate its contribution in antibiotics-integrating therapies, this study pharmacologically verified whether LHQW could alleviate lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI and explore its potential mechanisms in maintaining the physiology of macrophage-epithelial unit. In ALI mouse model, the pathological parameters, including the anal temperature, inflammation condition, lung edema, histopathological structures, have all been systematically analyzed. Results consistently supported the effectiveness of the combined strategy for LHQW and low-dose antibiotics. Furthermore, we established the macrophages-alveolar epithelial cells co-culture model and firstly proved that LHQW inhibited LPS-induced ER stress and TRAIL secretion in macrophages, thereby efficiently protected epithelial cells against TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Mechanistically, results showed that LHQW significantly deactivated NF-κB and reversed the SOCS3 expression in inflammatory macrophages. Furthermore, we proved that the therapeutic effects of LHQW were highly dependent on JNK-AP1 regulation. In conclusion, our data proved that LHQW is an epithelial protector in ALI, implying its promising potential in antibiotic alternative therapy.
Keywords: Lian Hua Qing Wen capsule; acute lung injury; endoplasmic reticulum stress; macrophages and epithelial cells; tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.
Copyright © 2020 Li, Ran, Sun, Yin, Luo, Liu, Zhao, Yang, Li, Chen, Weng, Wang, Cai and Zhu.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Network pharmacology analysis of the therapeutic mechanisms of the traditional Chinese herbal formula Lian Hua Qing Wen in Corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19), gives fundamental support to the clinical use of LHQW.Phytomedicine. 2020 Dec;79:153336. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153336. Epub 2020 Sep 6. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32949888 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Lian Hua Qing Wen capsules regulates the inflammatory response caused by M1 macrophage based on cellular experiments and computer simulations.Acta Trop. 2024 Sep;257:107320. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2024.107320. Epub 2024 Jul 14. Acta Trop. 2024. PMID: 39002739
-
[Efficacy and mechanism of Lianhua Qingwen Capsules(LHQW) on chemotaxis of macrophages in acute lung injury (ALI) animal model].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Jun;44(11):2317-2323. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190210.001. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31359658 Chinese.
-
Mechanisms Underlying the Effects of Lianhua Qingwen on Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury: A Network Pharmacology Approach.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 14;12:717652. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.717652. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34721017 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T cell and macrophage crosstalk in acute lung injury: future perspectives.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jan 16;9(1):9. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01310-7. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 36646692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of lung macrophages in acute respiratory distress syndrome.Inflamm Res. 2022 Dec;71(12):1417-1432. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01645-4. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36264361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in Traditional Chinese Medicine Against Respiratory Viruses: A Review.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 31;12:743623. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.743623. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34531754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effect of Fluorofenidone Against Acute Lung Injury Through Suppressing the MAPK/NF-κB Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 20;12:772031. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.772031. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34987397 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal medicine: Fighting SARS-CoV-2 infection on all fronts.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 24;270:113869. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113869. Epub 2021 Jan 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33485973 Free PMC article.
-
All‑trans retinoic acid promotes macrophage phagocytosis and decreases inflammation via inhibiting CD14/TLR4 in acute lung injury.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Dec;24(6):868. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12508. Epub 2021 Oct 22. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34676874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dong L., Xia J.-w., Gong Y., Chen Z., Yang H.-h., Zhang J., et al. (2014). Effect of Lianhuaqingwen Capsules on Airway Inflammation in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 1–11. 10.1155/2014/637969 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

