A Novel Peptide Antibiotic Produced by Streptomyces roseoflavus Strain INA-Ac-5812 With Directed Activity Against Gram-Positive Bacteria
- PMID: 33072016
- PMCID: PMC7533577
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.556063
A Novel Peptide Antibiotic Produced by Streptomyces roseoflavus Strain INA-Ac-5812 With Directed Activity Against Gram-Positive Bacteria
Abstract
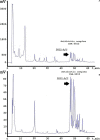
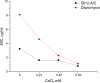
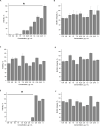
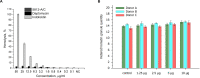
In this work, we report the isolation and detailed functional characterization for the new non-ribosomally synthesized antibiotic 5812-A/C, which was derived from metabolites of Streptomyces roseoflavus INA-Ac-5812. According to its chemical structure, the studied 5812-A/C preliminary is composed of a cyclic peptide part covalently bounded with an arabinose residue. N-terminal amino acid sequencing of the native peptide has identified its partial structure of Leu-Asp-Gly-Ser-Gly and consisting of a Tyr residue that is supposed to have a two-component peptide nature for the molecule studied. However, the structural analysis of the antibiotic complex derived from S. roseoflavus INA-Ac-5812 is still ongoing. The mechanism of action of 5812-A/C was assessed in comparison with its most related analog, the lipopeptide antibiotic daptomycin, given the presence in both antimicrobials of an L-kynurenine amino acid residue. The inhibitory activity of 5812-A/C against Gram-positive bacteria including methicillin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus was similar to daptomycin. The mechanism of action of 5812-A/C was associated with the disruption of membrane integrity, which differs in comparison with daptomycin and is most similar to the antimicrobial membrane-disturbing peptides. However, 5812-A/C demonstrated a calcium-dependent mode of action. In addition, unlike daptomycin, 5812-A/C was able to penetrate mature biofilms and inhibit the metabolic activity of embedded S. aureus cells. At the same time, 5812-A/C has no hemolytic activity toward erythrocyte, but possessed weak cytotoxic activity represented by heterochromatin condensation in human buccal epithelium cells. The biological properties of the peptide 5812-A/C suggest its classification as a calcium-dependent antibiotic effective against a wide spectrum of Gram-positive pathogenic bacteria.
Keywords: Streptomyces roseoflavus; anti-biofilm action; calcium-depending antibiotic; daptomycin; lipoglycopeptide antibiotic; peptide antibiotic.
Copyright © 2020 Vasilchenko, Julian, Lapchinskaya, Katrukha, Sadykova and Rogozhin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Staphylococcus aureus is able to generate resistance to novel lipoglycopeptide antibiotic gausemycin A.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 29;13:963979. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.963979. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36246291 Free PMC article.
-
Gain-of-Function Mutations in the Phospholipid Flippase MprF Confer Specific Daptomycin Resistance.mBio. 2018 Dec 18;9(6):e01659-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01659-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30563904 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial mechanism of daptomycin antibiotic against Staphylococcus aureus based on a quantitative bacterial proteome analysis.J Proteomics. 2017 Jan 6;150:242-251. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.09.014. Epub 2016 Sep 29. J Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 27693894
-
Lipopeptides, focusing on daptomycin, for the treatment of Gram-positive infections.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2004 Sep;13(9):1159-69. doi: 10.1517/13543784.13.9.1159. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15330747 Review.
-
Daptomycin: a lipopeptide antibiotic for the treatment of serious Gram-positive infections.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005 Mar;55(3):283-8. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkh546. Epub 2005 Feb 10. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15705644 Review.
Cited by
-
Quorum Quenching Approaches against Bacterial-Biofilm-Induced Antibiotic Resistance.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 3;13(7):619. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070619. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A peptide encoded by a highly conserved gene belonging to the genus Streptomyces shows antimicrobial activity against plant pathogens.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Oct 5;14:1250906. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1250906. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37868322 Free PMC article.
-
Gausemycin A-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Demonstrates Affected Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Homeostasis.Microorganisms. 2023 May 18;11(5):1330. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051330. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37317304 Free PMC article.
-
Recently Discovered Secondary Metabolites from Streptomyces Species.Molecules. 2022 Jan 28;27(3):887. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030887. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of diverse biosynthetic secondary metabolites gene clusters using genome mining of indigenous Streptomyces strains isolated from saline soils in Iran.Iran J Microbiol. 2022 Dec;14(6):881-890. doi: 10.18502/ijm.v14i6.11263. Iran J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36721452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alferova V. A., Shuvalov M. V., Novikov R. A., Trenin A. S., Dezhenkova L. G., Gladkikh E. G., et al. (2019). Structure-activity studies of irumamycin type macrolides from Streptomyces sp. INA-Ac-5812. Tetrahedron Lett. 60 1448–1451. 10.1016/j.tetlet.2019.04.051 - DOI
-
- Boudjemaa R., Briandet R., Revest M., Jacqueline C., Caillon J., Fontaine-Aupart M. P., et al. (2016). New insight into daptomycin bioavailability and localization in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms by dynamic fluorescence imaging. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60 4983–4990. 10.1128/AAC.00735-16 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

