Deltaproteobacteria and Spirochaetes-Like Bacteria Are Abundant Putative Mercury Methylators in Oxygen-Deficient Water and Marine Particles in the Baltic Sea
- PMID: 33072037
- PMCID: PMC7536318
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.574080
Deltaproteobacteria and Spirochaetes-Like Bacteria Are Abundant Putative Mercury Methylators in Oxygen-Deficient Water and Marine Particles in the Baltic Sea
Abstract
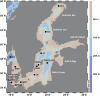
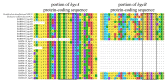
Methylmercury (MeHg), a neurotoxic compound biomagnifying in aquatic food webs, can be a threat to human health via fish consumption. However, the composition and distribution of the microbial communities mediating the methylation of mercury (Hg) to MeHg in marine systems remain largely unknown. In order to fill this knowledge gap, we used the Baltic Sea Reference Metagenome (BARM) dataset to study the abundance and distribution of the genes involved in Hg methylation (the hgcAB gene cluster). We determined the relative abundance of the hgcAB genes and their taxonomic identity in 81 brackish metagenomes that cover spatial, seasonal and redox variability in the Baltic Sea water column. The hgcAB genes were predominantly detected in anoxic water, but some hgcAB genes were also detected in hypoxic and normoxic waters. Phylogenetic analysis identified putative Hg methylators within Deltaproteobacteria, in oxygen-deficient water layers, but also Spirochaetes-like and Kiritimatiellaeota-like bacteria. Higher relative quantities of hgcAB genes were found in metagenomes from marine particles compared to free-living communities in anoxic water, suggesting that such particles are hotspot habitats for Hg methylators in oxygen-depleted seawater. Altogether, our work unveils the diversity of the microorganisms with the potential to mediate MeHg production in the Baltic Sea and pinpoint the important ecological niches for these microorganisms within the marine water column.
Keywords: Baltic Sea; deltaproteobacteria; hgcAB; mercury methylation; spirochaetes-like bacteria.
Copyright © 2020 Capo, Bravo, Soerensen, Bertilsson, Pinhassi, Feng, Andersson, Buck and Björn.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Redox gradient shapes the abundance and diversity of mercury-methylating microorganisms along the water column of the Black Sea.mSystems. 2023 Aug 31;8(4):e0053723. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00537-23. Epub 2023 Aug 14. mSystems. 2023. PMID: 37578240 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrospina-Like Bacteria Are Potential Mercury Methylators in the Mesopelagic Zone in the East China Sea.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jul 3;11:1369. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01369. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32719662 Free PMC article.
-
Periphyton and Flocculent Materials Are Important Ecological Compartments Supporting Abundant and Diverse Mercury Methylator Assemblages in the Florida Everglades.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Jun 17;85(13):e00156-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00156-19. Print 2019 Jul 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31028023 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Mercury Methylation in Aquatic Environments: A Critical Review of Published Field and Laboratory Studies.Environ Sci Technol. 2019 Jan 2;53(1):4-19. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b02709. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Environ Sci Technol. 2019. PMID: 30525497 Review.
-
Microbial mercury transformations: Molecules, functions and organisms.Adv Appl Microbiol. 2022;118:31-90. doi: 10.1016/bs.aambs.2022.03.001. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35461663 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential for mercury methylation by Asgard archaea in mangrove sediments.ISME J. 2023 Mar;17(3):478-485. doi: 10.1038/s41396-023-01360-w. Epub 2023 Jan 13. ISME J. 2023. PMID: 36639538 Free PMC article.
-
Redox gradient shapes the abundance and diversity of mercury-methylating microorganisms along the water column of the Black Sea.mSystems. 2023 Aug 31;8(4):e0053723. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00537-23. Epub 2023 Aug 14. mSystems. 2023. PMID: 37578240 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advance of microbial mercury methylation in the environment.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Feb 26;108(1):235. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12967-6. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38407657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contrasting diversity and temporal patterns in leaf and root microbiome of two nearby temperate Zostera marina meadows.Environ Microbiome. 2025 Aug 5;20(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s40793-025-00760-z. Environ Microbiome. 2025. PMID: 40765019 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolically diverse microorganisms mediate methylmercury formation under nitrate-reducing conditions in a dynamic hydroelectric reservoir.ISME J. 2023 Oct;17(10):1705-1718. doi: 10.1038/s41396-023-01482-1. Epub 2023 Jul 26. ISME J. 2023. PMID: 37495676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alldredge A. L., Silver M. W. (1988). Characteristics, dynamics and significance of marine snow. Prog. Oceanogr. 20 41–82. 10.1016/0079-6611(88)90053-5 - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

