Development of PMAxxTM-Based qPCR for the Quantification of Viable and Non-viable Load of Salmonella From Poultry Environment
- PMID: 33072053
- PMCID: PMC7536286
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.581201
Development of PMAxxTM-Based qPCR for the Quantification of Viable and Non-viable Load of Salmonella From Poultry Environment
Abstract
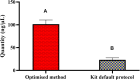
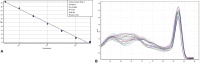
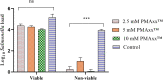
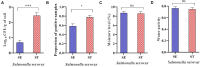
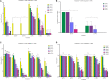
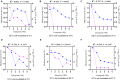
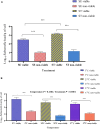
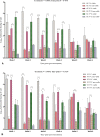
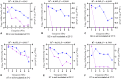
Determining the viable and non-viable load of foodborne pathogens in animal production can be useful in reducing the number of human outbreaks. In this study, we optimized a PMAxxTM-based qPCR for quantifying viable and non-viable load of Salmonella from soil collected from free range poultry environment. The optimized nucleic acid extraction method resulted in a significantly higher (P < 0.05) yield and quality of DNA from the pure culture and Salmonella inoculated soil samples. The optimized primer for the amplification of the invA gene fragment showed high target specificity and a minimum detection limit of 102 viable Salmonella from soil samples. To test the optimized PMAxxTM-based qPCR assay, soil obtained from a free range farm was inoculated with Salmonella Enteritidis or Salmonella Typhimurium, incubated at 5, 25, and 37°C over 6 weeks. The survivability of Salmonella Typhimurium was significantly higher than Salmonella Enteritidis. Both the serovars showed moisture level dependent survivability, which was significantly higher at 5°C compared with 25°C and 37°C. The PMAxxTM-based qPCR was more sensitive in quantifying the viable load compared to the culture method used in the study. Data obtained in the current study demonstrated that the optimized PMAxxTM-based qPCR is a suitable assay for quantification of a viable and non-viable load of Salmonella from poultry environment. The developed assay has applicability in poultry diagnostics for determining the load of important Salmonella serovars containing invA.
Keywords: PMAxx-based qPCR; Salmonella contamination; Salmonella load; poultry production; viability assay.
Copyright © 2020 Zhang, Khan and Chousalkar.
Figures
References
-
- Bellehumeur C., Boyle B., Charette S. J., Harel J., L’homme Y., Masson L., et al. (2015). Propidium monoazide (PMA) and ethidium bromide monoazide (EMA) improve DNA array and high-throughput sequencing of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus identification. J. Virol. Methods 222 182–191. 10.1016/j.jviromet.2015.06.014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cools D., Merckx R., Vlassak K., Verhaegen J. (2001). Survival of E. coli and Enterococcus spp. derived from pig slurry in soils of different texture. Appl. Soil Ecol. 17 53–62. 10.1016/s0929-1393(00)00133-5 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

